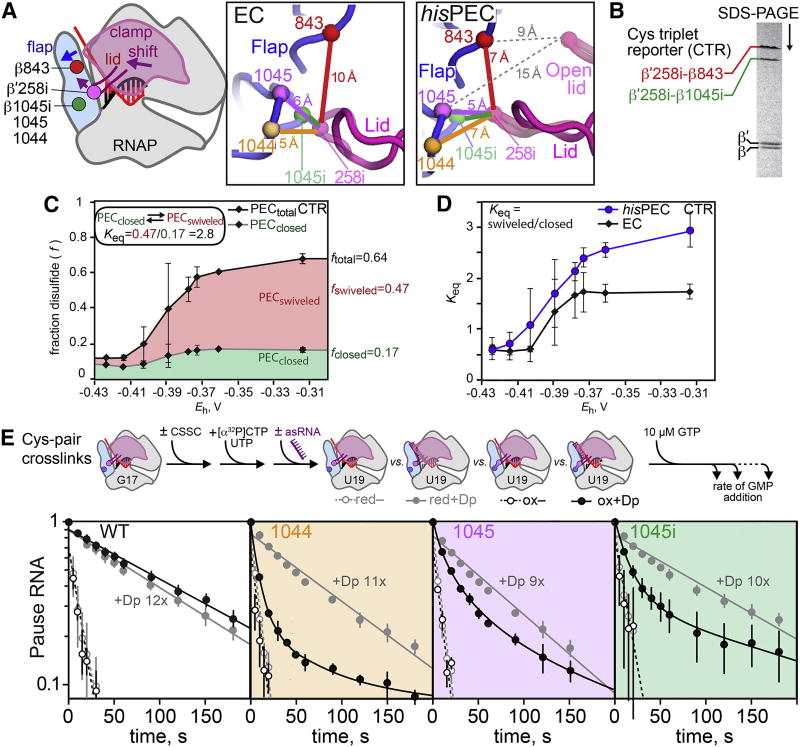
Figure 5. The PH induced modest clamp swiveling to increase pause lifetime.
(A) Disulfides used to probe changes in clamp position in the hisPEC shown on an EC cartoon, the EC exit channel (6ALF), and the hisPEC exit channel (6ASX). A single Cys insertion between β′257 and 258 in the lid (258i) was paired with different flap Cys substitutions (1044, 1045, and 1045i) and with two flap Cys residues (1045i and 843) in the Cys-triplet reporter (CTR). The distances between Cα atoms of the different Cys pairs are shown in colored lines, and the distance between 258i and flap Cys residues in the open clamp conformation of 4GZY (Weixlbaumer et al., 2013) are shown as grey dotted lines.
(B) The alternative disulfide bonds in the CTR can be distinguished by non-reducing SDS-PAGE.
C. Redox titration of the CTR on a hisPEC scaffold using DTT-cystamine mixtures (see Methods).
(D) The ratio of the swiveled (258i-843) disulfide to the closed (258i-1045i) disulfide in CTR RNAP on the hisPEC and EC scaffolds.
(E) The effect of disulfide bonds on RNA duplex-stimulation of pausing. An exit channel duplex formed with an 8mer antisense RNA is known to mimic the effect of the his PH (Dp, exit-channel duplex).