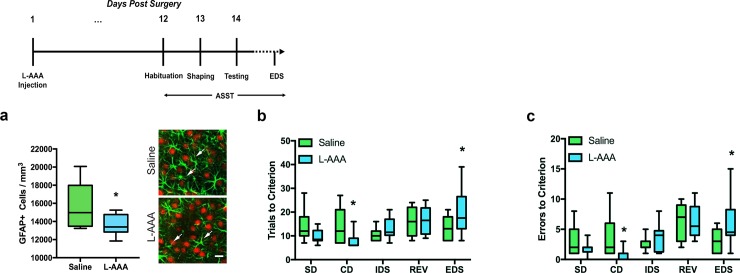
Fig 1. Reduction of astrocyte number in the mPFC impairs cognitive flexibility.
Rats were infused with either L-AAA (n = 12) or saline (n = 11) in the mPFC 12 days before completing the ASST. L-AAA treatment altered mPFC-dependent performance on the extradimensional shift (EDS). A timeline for the L-AAA behavioral experiment is provided above. a. L-AAA treatment significantly reduced the number of GFAP+ astrocytes in the mPFC. Confocal images of GFAP+ (green) and NeuN+ (red) staining 13 days after treatment with either L-AAA or saline. Scale bar = 20 μm. * p<0.05 compared to saline-infused controls. Arrows point to either the presences or absence of GFAP+ staining in green. b. Rats with fewer astrocytes in the mPFC took fewer trials to reach criterion for the compound discrimination (CD) compared to saline-infused controls but more trials to reach criterion on the EDS portion of the task when compared to saline controls. c. Rats with fewer astrocytes also made fewer errors on the CD, but more errors on the EDS compared to saline-infused controls.