Figure 1.
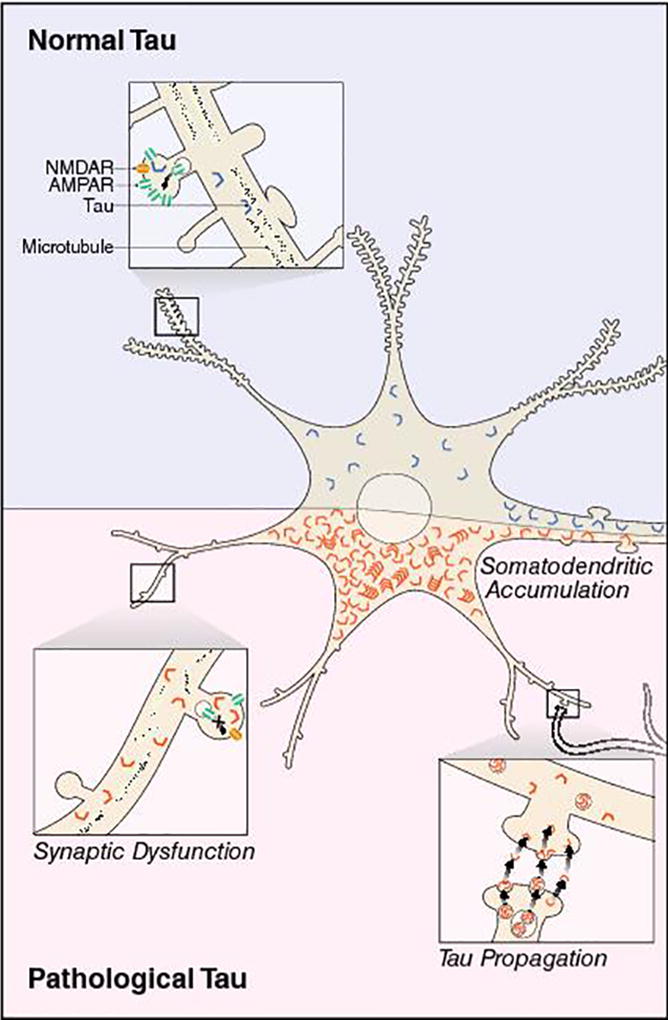
Pathological tau at synapses in AD. In normal conditions, tau is predominantly localized in axons, but it can also be found at synapses. In disease, pathogenic tau is missorted and accumulates in the somatodendritic compartment of neurons. The buildup of toxic tau can affect synaptic transmission by downregulating postsynaptic AMPA-type glutamate receptors and blocking the expression of synaptic plasticity. Pathogenic tau can also promote the loss of dendritic spines. The propagation of toxic tau among neurons could be trans-synaptic and induced by activity, but the mechanism for tau release is still unclear.
