Figure 2.
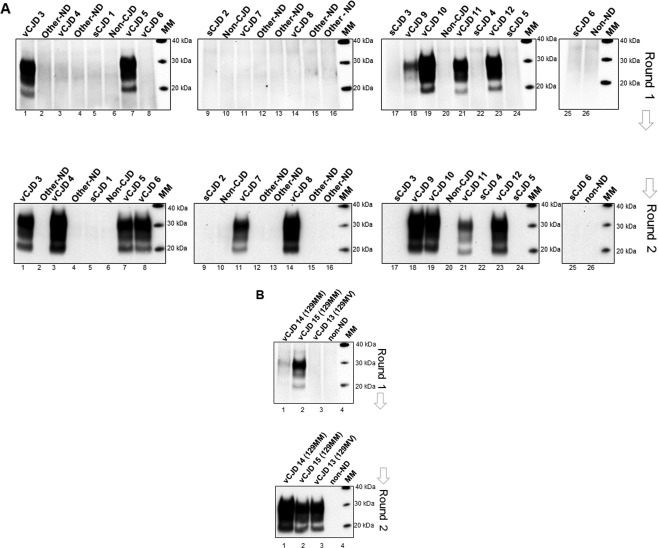
Detection of vCJD prions in CSF samples in a larger blinded panel of PRNP‐codon 129MM and MV cases by hsPMCA. (A) A second blinded panel of CSF samples were evaluated including 10 definite vCJD codon 129MM (vCJD 3–12), 6 sCJD MM1 (sCJD 1–6), and 10 CSF controls from other neurodegenerative diseases (Other–ND), non‐CJD (non‐CJD), and non‐neurodegenerative diseases (non‐ND). A volume of 7.5 μl of CSF (for each sample) was mixed with 92.5 μl volumes of substrate and subjected to amplification. (B) Analysis of two vCJD PRNP‐codon 129MM cases, one possible (vCJD 14) and one probable (vCJD 15), a definite vCJD codon 129MV case reported recently in the United Kingdom (vCJD 13), and one non‐neurodegenerative (non‐ND) control were evaluated by hsPMCA. Two amplification rounds were completed (Round 1 and 2). Samples were treated with Proteinase K and evaluated by Western blotting using 3F4 mAb. The molecular mass of electrophoretic markers (MM) is shown. [N = 30; 13 vCJD (definite, possible and probable), 6 sCJD, 5 non‐ND, 6 Other‐ND].
