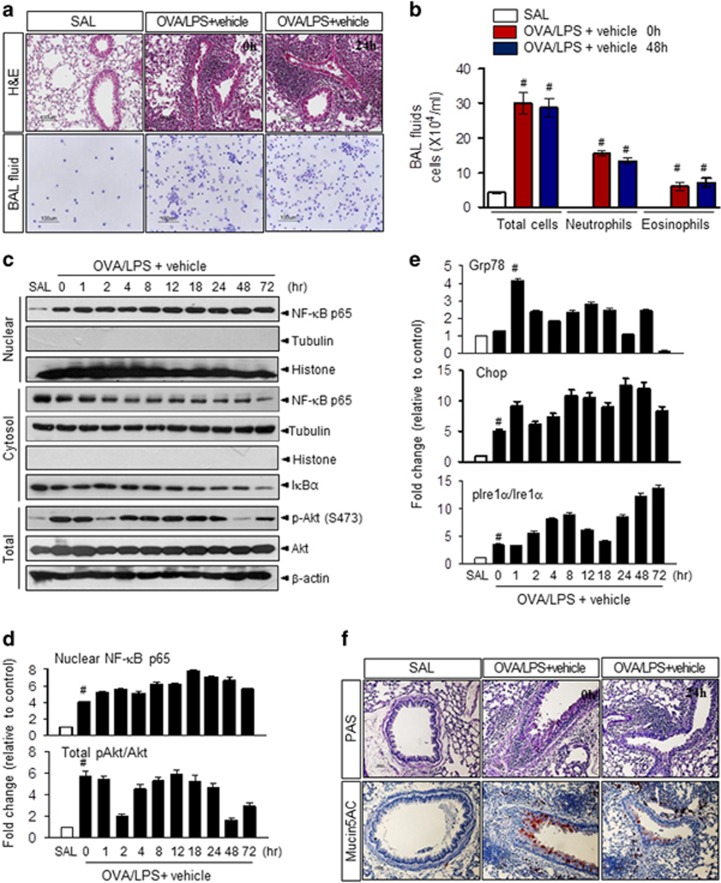
Figure 1.
Ovalbumin (OVA) plus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces severe asthma in mice. (a) Lung tissues and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) cells obtained from OVA/LPS-sensitized/challenged mice (OVA/LPS), saline/saline-sensitized/challenged mice (SAL) and OVA/LPS-sensitized/challenged mice administered drug and vehicle were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (upper) and Diff-Quick solution (lower). Magnification, × 100. (b) Total cells and differential cellular components of BALF (n=6 animals per experimental group. (c) Immunoblotting of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), IκBα and AKT proteins from samples collected by subcellular fractionation of lung tissues. (d) Changes in the NF-κB and AKT protein expression levels (mean±s.e.m.) relative to the control (SAL) group (n=6 animals per group). (e) Changes in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress marker protein expression (mean±s.e.m.) relative to the control (SAL) group (n=6 animals per group). (f) Lung sections from mice were prepared and stained with periodic acid–Schiff (PAS; upper) and anti-mucin5AC antibody (lower). Mice challenged with saline (SAL) were used as the control group. #P<0.05 versus SAL.