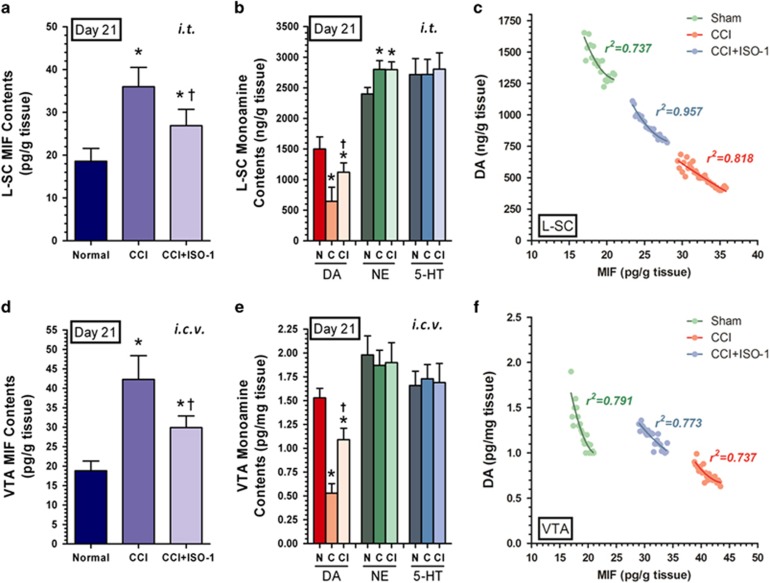
Figure 4.
Effects of ISO-1 on migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and monoamine content in L-SC and VTA following chronic constriction injury (CCI). The MIF inhibitor ISO-1 was administered i.t. or i.c.v. for 2 weeks from day 7 post-nerve injury. In L-SC and VTA, the MIF and monoamine content was detected with ELISA and HPLC, respectively, at post-injury day 21. The turnover effect of i.t. ISO-1 for MIF and dopamine in L-SC is shown in a and b (*P<0.05 vs normal mice; †P<0.05 vs CCI mice). In VTA, a similar turnover phenomenon of i.c.v. ISO-1 regarding MIF and dopamine was also observed (d, e, *P<0.05 vs normal mice; †P<0.05 vs CCI mice). Data are shown as the means±s.e.m.’s and were analyzed with one-way ANOVA. N=15 in each group. Then, correlation analysis clearly showed an obvious non-linear, negative relationship between MIF and dopamine in L-SC and VTA in sham, CCI, or CCI+ISO-1 mice (c, f). C, CCI; CI, CCI+ISO-1; L-SC, lumbar spinal cord L5-6; N, normal; VTA, ventral tegmental area.