Figure 3. R. solanacearum enriches putrescine in xylem sap and culture medium.
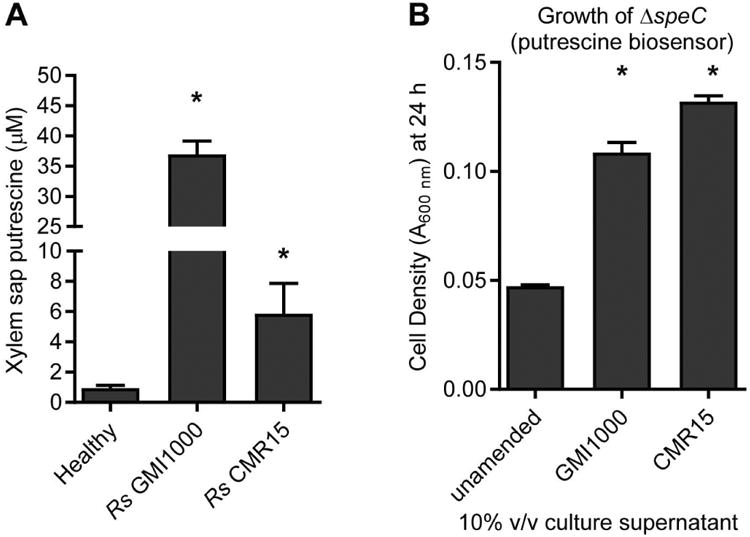
(A) Xylem sap was harvested at symptom onset from tomato plants (cv. Money Maker) infected with R. solanacearum strains; water-inoculated plants served as controls. Putrescine was measured by LC-MS. (B) Putrescine in spent culture supernatant was detected by growth of the GMI1000 ΔspeC mutant, a sensitive putrescine biosensor as shown in Figure 4. R. solanacearum strains were grown in minimal medium (MM) for 24 h. Culture supernatants were filter-sterilized and added to fresh MM at 10% v/v and inoculated with ΔspeC. Growth of ΔspeC mutant was measured at 24 h. Values are mean ± SEM. (*P<0.05 vs. healthy, t-test with Holm-Bonferroni correction, n≥3 pools).
