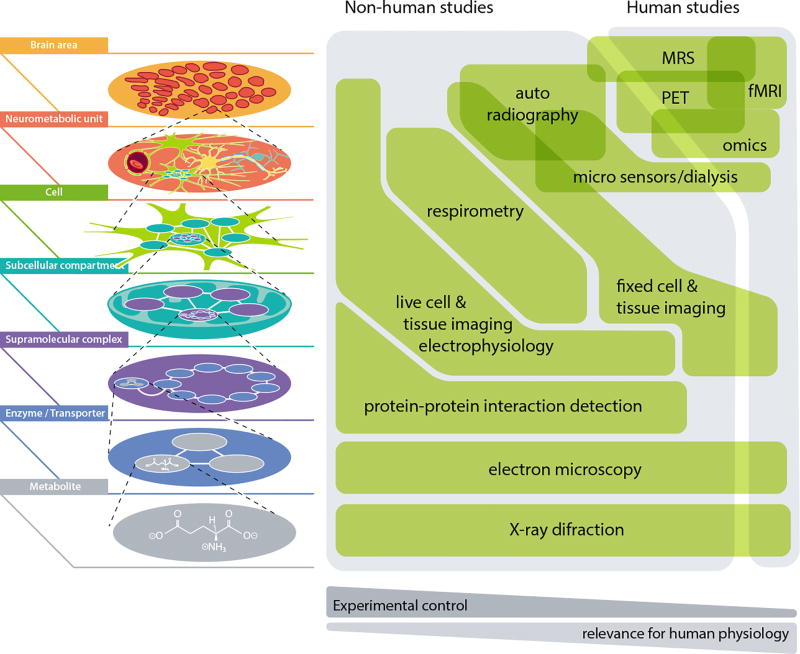
Figure 2. Technical domains in brain energy metabolism research.
Different techniques perform over different domains, which are in turn defined by a combination of organizational level, experimental control and relevance to human physiology. For example, electrophysiology achieves excellent experimental control at small and intermediate hierarchies by in vitro recording from single channels, single cells or small cell assemblies, but it is not practical in vivo and cannot be used in humans. MRS, in contrast, may be applied to human subjects, but has limited experimental control and provides time- and space-averaged measurements.