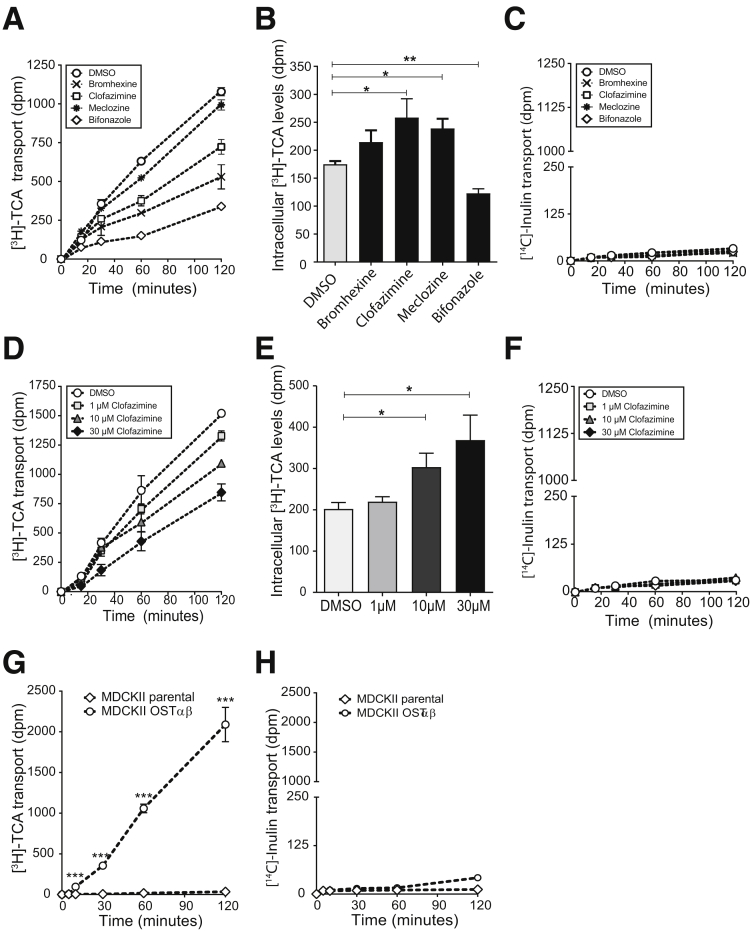
Figure 4.
Transcellular transport of taurocholic acid across MDCKII monolayers. (A) Time profile for taurocholic acid transport across MDCKII monolayers expressing ASBT and OSTα-OSTβ. Cells were treated with 10 μmol/L bromhexine HCl, clofazimine, meclozine 2HCl, or bifonazole for 1 hour before the experiment and during the 2 hours of the experiment when taurocholic acid was added and measured. (B) Intracellular levels of taurocholic acid 2 hours after addition of apical taurocholic acid when treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 10 μmol/L bromhexine HCl, clofazimine, meclozine 2HCl, and bifonazole. (C) Disintegrations per minute of [14C]-inulin after 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes of transport in MDCKII cells administered with bromhexine, clofazimine, meclizine, bifonazole, or DMSO (0.01%). (D) Time profile for transcellular transport of taurocholate from the apical to basolateral compartment after treatment with 1, 10, or 30 μmol/L clofazimine. (E) Increased intracellular levels of taurocholate in MDCKII cells after 2 hours uptake in cells treated with 1, 10, or 30 μmol/L clofazimine. (F) Disintegrations per minute of [14C]-inulin after 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes of transport in MDCKII cells administered with 1, 10, and 3 μmol/L clofazimine or DMSO (0.03%). (G) Apical to basolateral [3H]-taurocholic acid transport in MDCKII parental cells vs MDCKII cells expressing OSTα-OSTβ. (H) [14C]-inulin transport in MDCKII parental cells vs MDCKII-OSTαβ cells. Data are represented as means ± SD. Data are from a representative experiment replicated 2 times (n = 3). *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001. (A–F) One-way analysis of variance; post hoc: Dunnett multiple comparison; (G and H) Student t test, 2-tailed.