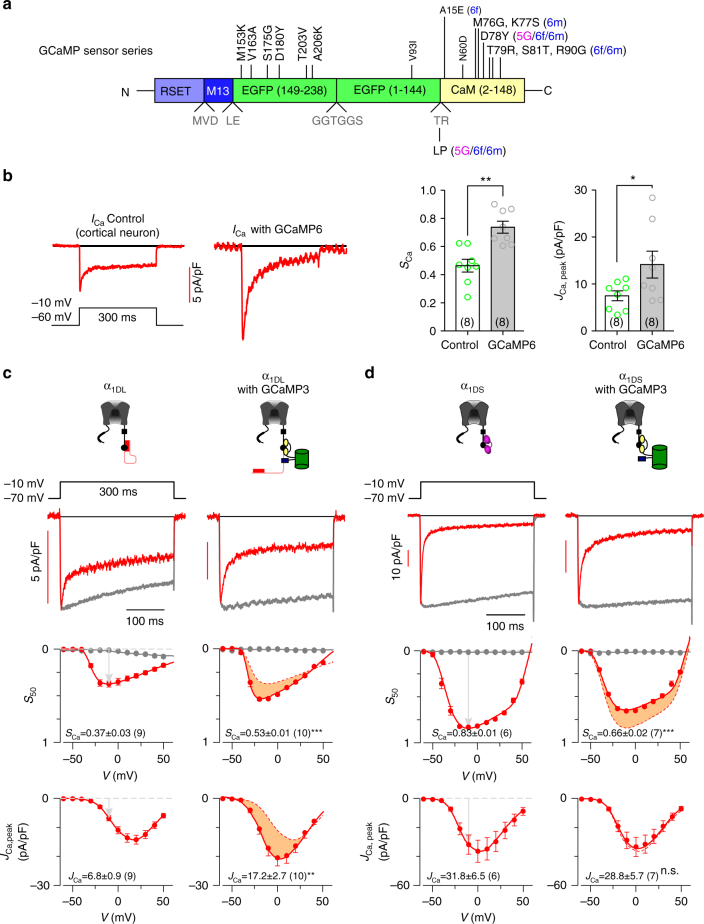
Fig. 2.
GCaMP interferes with CaV1.3 gating. a Schematic summary of GCaMP series. Upgrades of GCaMP (from GCaMP3 to GCaMP5 and GCaMP6) were achieved by mutations of the EGFP and CaM domains at the sites indicated by vertical letters (GCaMP3 vs. GCaMP), or by horizontal letters (GCaMP5G/6f/6m vs. GCaMP3). Details see Supplementary Fig. 1. b Effects on ICa were examined for neurons infected with AAV-Syn-GCaMP6f. Representative traces of Ca2+ current (left), SCa and JCa analyses (right) for native CaV1.3 in cortical neurons expressing GCaMP6. Neurons were treated with a cocktail recipe to isolate CaV1 current (mostly CaV1.3) and recorded at the membrane potential (V) of −10 mV. SCa (quantified as 1−ICa,50 /ICa, peak, where ICa,50 and ICa, peak represent the currents measured at 50 ms and the instantaneous peak, respectively) and JCa (pA/pF, the current density of ICa, peak) serve as the indices for CDI and VGA respectively. c Effects of GCaMP3 on recombinant α1DL. Representative Ca2+ current traces were compared for ICa recorded from HEK293 cells expressing long variant α1DL alone (left), or with GCaMP3 (right) at −10 mV. Ba2+ currents (rescaled) and Ca2+ currents (ICa) were shown as grey and red traces, respectively, with scale bars indicative of ICa amplitudes. CDI (SCa) and VGA (JCa) profiles at different membrane potentials are compared between α1DL control and α1DL overexpressed with GCaMP3 (differences highlighted by orange areas). d Effects of GCaMP3 on recombinant α1DS alone (left), or with GCaMP3 (right), in a similar fashion to c. Standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) and Student’s t-test (two-tailed unpaired with criteria of significance: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 and, ***p < 0.001) were calculated when applicable, and n.s. denotes “not significant”