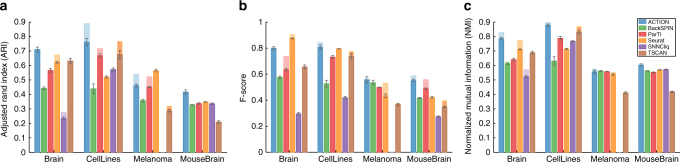
Fig. 5.
Performance of ACTION in identifying discrete cell types. ACTION identifies cell types by classifying cells according to their dominant primary function (closest archetype). Performance is measured via various measures with respect to the cell types provided with the data: a Adjusted Rand Index (ARI), b F-score, and c Normalized Mutual Information (NMI) of cell-type identification. Larger values are better, and the perfect score (upper bound) is one. Lighter shades are the actual results when using all cells/ samples, whereas the darker bar and the error bar indicates the standard error in a 10-fold test to estimate the variability and stability of predictions for each method. In the CellLines dataset, which was originally created to benchmark cell-type identification methods, ACTION outperforms other methods with respect to ARI and NMI measures, and ties with Seurat in terms of F-score. In the MouseBrain dataset, ACTION significantly outperforms other methods in all three measures. In the Brain datasets there is a competition between ACTION and Seurat, whereas in the Melanoma there is more variability among different methods. This is particularly associated with the level of annotations in this dataset (lack of annotations for T-cell subclasses and tumor subtypes, for example) and the varying resolution of different methods