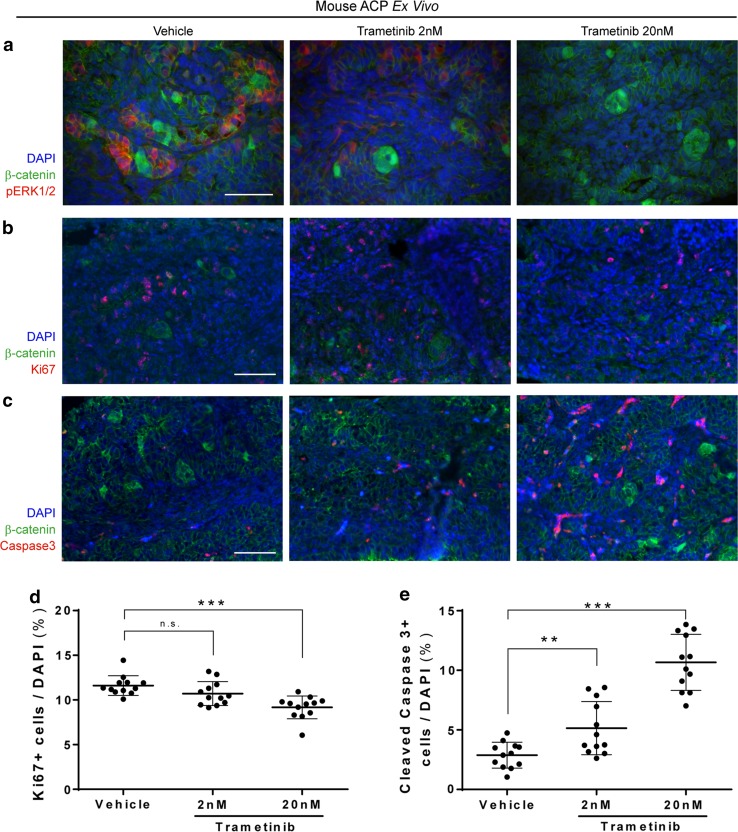
Fig. 6.
Ex vivo inhibition of the MAPK/ERK pathway in mouse ACP results in decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis of tumour cells. Neoplastic pituitaries of the ACP embryonic mouse model were cultured in the presence of the MEK inhibitor trametinib (2 or 20 nM) or the vehicle control (DMSO) for 18 h. Following histological processing, sections were immunostained against β-catenin and pERK1/2 (readout of active MAPK/ERK pathway; a), Ki-67 (proliferation marker; b) and cleaved caspase-3 (apoptosis marker; c). Quantitative analysis showing a significant dose-dependent reduction in Ki-67 proliferative index (d; 20 nM) and an increase in apoptosis (e; 2 and 20 nM) in trametinib-treated relative to vehicle-treated control. Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s post-test **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Mean of 4.1 × 103 nuclei for each point. Scale bars 50 μm