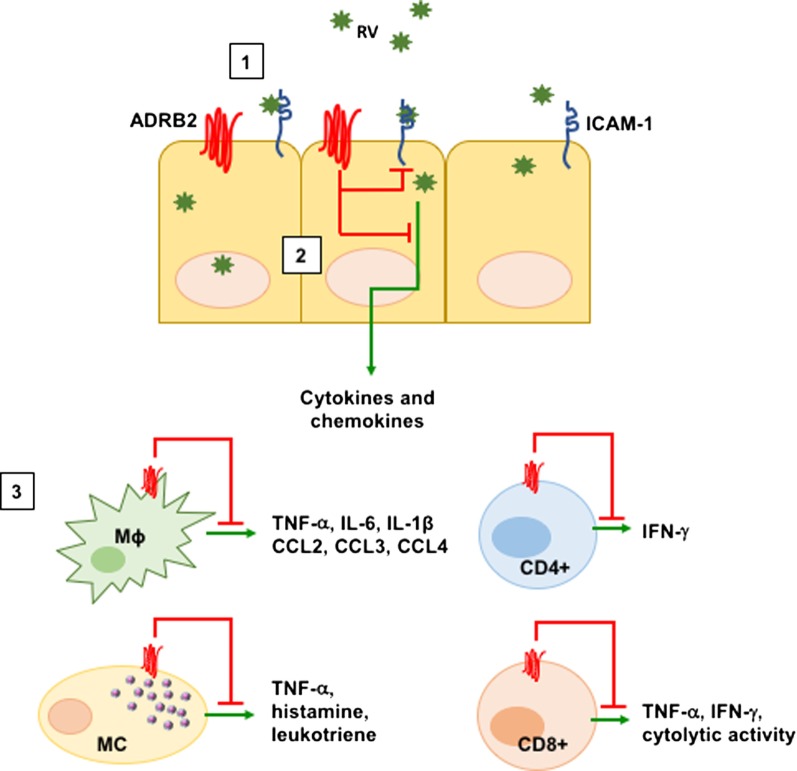
Figure 1.
ADRB2-mediated suppression of inflammatory processes. Adrenergic signaling through the ADRB2 inhibits various virus-induced immune mediators. [1] Rhinovirus (RV) infects the upper airways by binding to ICAM-1 on the surface of lung ECs. RV infection of ECs upregulates ICAM-1 as well as IL-8, IL-6, CCL5, CCL11, and CXCL10 to recruit inflammatory cells. [2] Activation of the ADRB2 by either the natural ligands epinephrine and norepinephrine or by β2-agonists downregulates ICAM-1 as well as IL-8, CCL5, and GM-CSF from ECs. [3] ADRB2 signaling additionally inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators in innate and adaptive immune cells. Abbreviations: EC, epithelial cell; MC, mast cell; Mɸ, macrophage.