Figure 2.
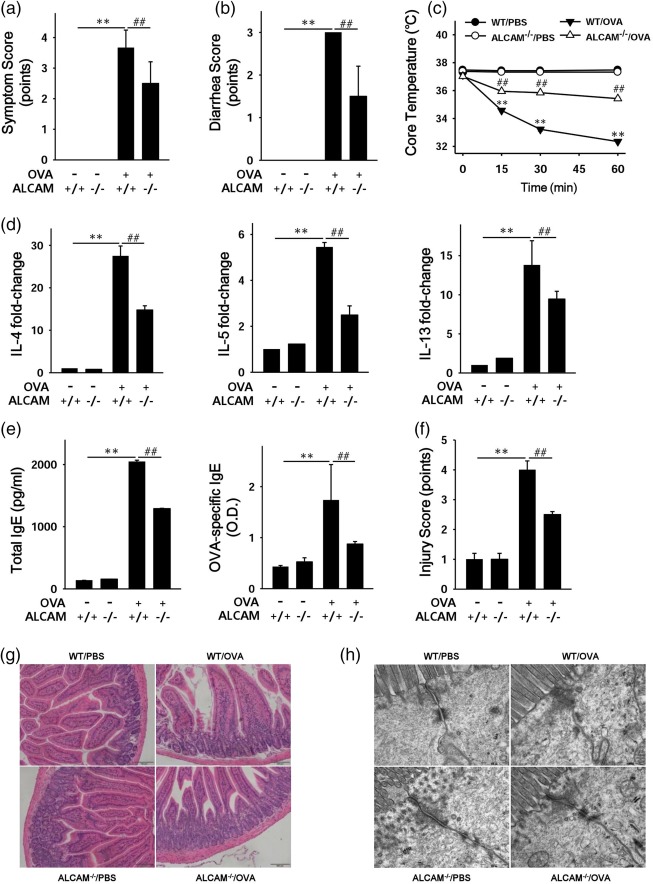
Activated leucocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM) regulates immune responses in a murine model of food allergy. Mice were sensitized with 50 µg of ovalbumin (OVA) and 10 µg of cholera toxin (CT) and challenged with 50 mg of OVA. After the last challenge, clinical score (a), diarrhoea score (b) and core temperature (c) were measured in OVA‐challenged wild‐type (WT) and ALCAM–/– mice (data are representative of three independent experiments, n = 4 for each group). (d) The mRNA expression of T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokine [interleukin (IL)‐4, IL‐5 and IL‐13] in the small intestine of the mice. (e) Levels of total immunoglobulin (Ig)E and optical density (OD) values of OVA‐specific IgE in mouse serum were measured by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for each group of mice (n = 5 for each group) in triplicate for each sample. Histological observations of the small intestine (f) and injury score (data representative of three independent experiments, n = 4 for each group) (g). (h) Morphological observations of intestinal tight junctions by electron microscopy (EM). **P < 0·01 [phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS) versus WT/OVA)]; ## P < 0·01 (WT/OVA versus ALCAM–/–/OVA). Magnification: f, ×200; i, ×50 000. [Colour figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
