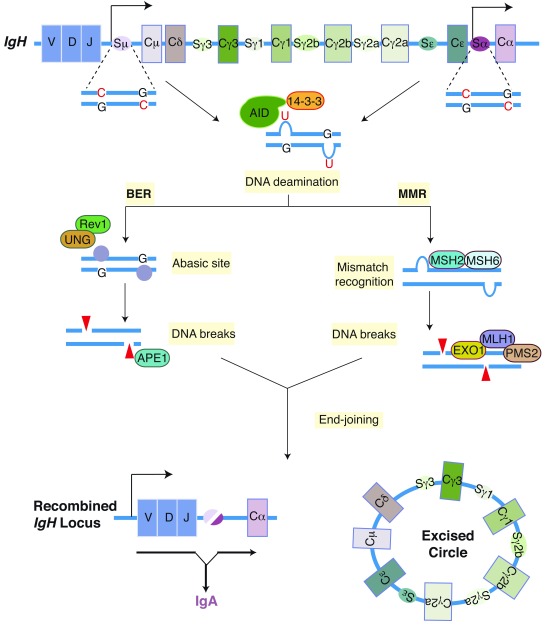
Figure 1. Mature B lymphocytes undergo class switch recombination (CSR) to alter the expression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region (C H).
The figure depicts CSR between Sμ and Sα in the immunoglobulin heavy chain ( IgH) locus. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) converts cytidines into uridines in S-region DNA. The dU:dG mismatch is converted into DNA double-strand breaks by either the base excision repair (BER) or the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway. In the BER pathway, uracil DNA glycosylase (UNG) removes the uracil base from the DNA to generate an abasic site, which is recognized and cleaved by the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1). During MMR, the dU:dG mismatch is recognized by mutS homologue 2 and mutS homologue 6 (MSH2 and MSH6), which recruit the complex of exonuclease 1 (EXO1), mutL homologue 1 (MLH1), and post-mitotic segregation 2 (PMS2) to excise a short patch of DNA that includes the dU:dG mismatch. The DNA breaks are ligated by classical or alternative non-homologous end-joining pathways to generate a recombined Igh locus and an excision circle. Rev1 and 14-3-3 are scaffolding proteins, which are necessary for the assembly of the protein complexes participating in CSR.