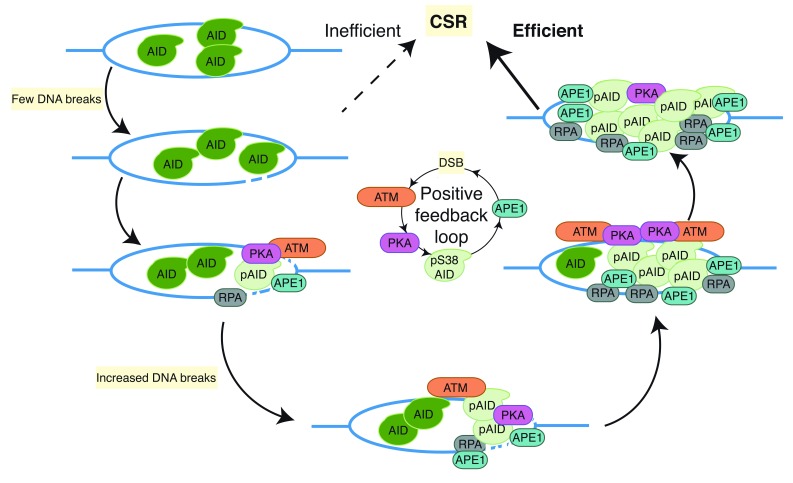
Figure 3. A hypothetical positive feedback loop generates a high density of DNA double-strand breaks to promote wild-type CSR.
AID-mediated deamination of S regions generates DNA breaks that induce PKA-dependent AID phosphorylation at serine-38 (pS38-AID) and subsequent binding of APE1 and RPA to pS38-AID. Recruitment of APE1 to S regions generates additional DNA breaks, inducing additional AID phosphorylation through an unidentified ATM-dependent mechanism of activating PKA. AID, activation-induced cytidine daminase; APE1, apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; CSR, class switch recombination; PKA, protein kinase A; RPA, replication protein A.