Fig. 2.
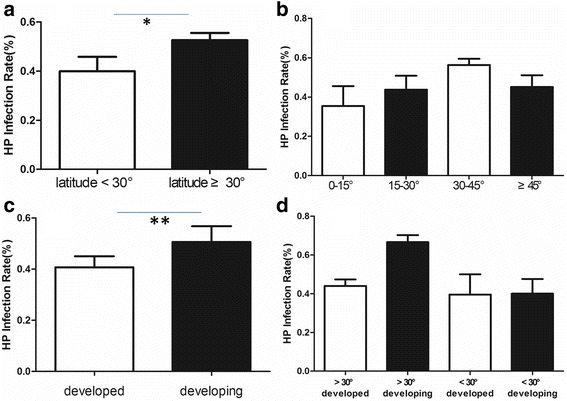
a Comparison of the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection between low and mid-to-high latitude zones (39.92% ± 21.15% vs. 52.56% ± 19.88%, *P = 0.05); b Comparisons of the prevalence of H. pylori infection in each 15°-latitude zone; c Comparison of the prevalence of H. pylori infection between developed and developing regions (43.48% ± 17.73% vs. 57.42% ± 21.76%, **P = 0.009); d Comparisons of the prevalence of H. pylori infection in developed countries and mid-to-high latitude zones, developing countries and mid-to-high latitude zones, developed countries and low latitude, developing countries and low latitude zones (P < 0.001)
