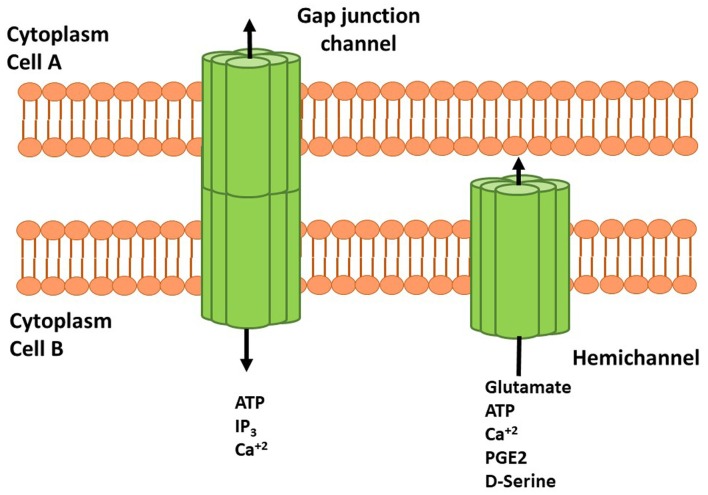
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of connexins (Cxs), hemichannels (HCs) and gap junctions (GJs) in cell membranes. HCs are transmembrane proteins composed of six connexin subunits that allow flow of several molecules and gliotransmitters from astrocyte to the extracellular space. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), glutamate, D-serine and prostaglandin (PG) E-2 can interact with their receptors and induce signaling cascades. Docking between two HCs or connexins forms GJ channels that allow the cell to cell communication mediated by ATP, inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate (IP3) and Ca2+. HCs and GJs activity modulate neuronal synaptic activity and plasticity.