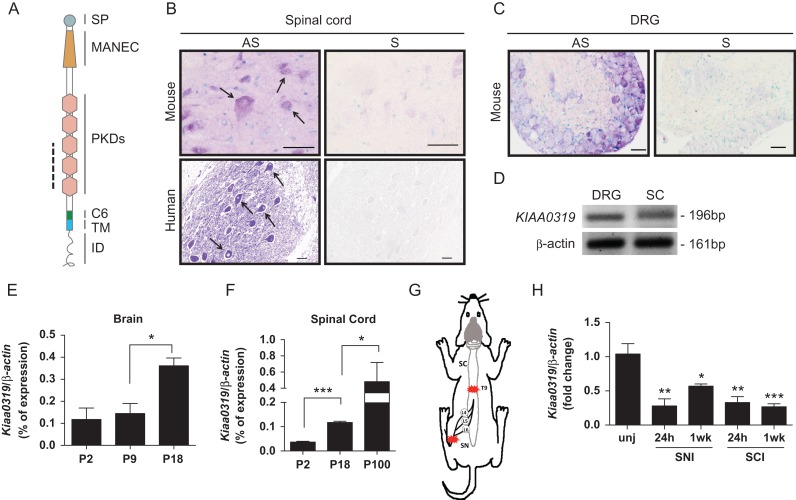
Figure 1.
Expression of Kiaa0319 in nervous tissue during development and after injury. (A) Schematic representation of KIAA0319 domains: SP, signal peptide; MANEC, motif at N-terminus with 8 cysteines; PKD; polycystic kidney disease; C6, domain with 6 cysteines; TM, transmembrane; ID, intracellular domain. The dashed line indicates the region corresponding to the in situ hybridization probe. (B) Representative microphotographs of in situ hybridization of Kiaa0319/KIAA0319 in ventral horn spinal cord neurons from mice (upper, P60, n = 4; scale bar, 20 μm) and human (lower, 33 years-old, n = 1; scale bar, 50 μm). AS, antisense probe; S, sense probe. Arrows in B highlight labeled neurons. (C) In situ hybridization of Kiaa0319 in mouse DRG (P20, n = 3). AS, antisense probe; S, sense probe; scale bar, 50 μm. (D) RT-PCR of KIAA0319 and β-actin (loading control) in human DRG and human spinal cord (SC) samples. (E, F) Quantitative-PCR analysis of the levels of Kiaa0319 expression in the mouse brain (E) and spinal cord (F) at postnatal days 2, 9, 18, and 100 (n = 4 each sample/age). (G) Schematic representation of the lesion model used to assess Kiaa0319 expression. L4, L5, and L6 DRGs were collected 24 h or 1 week after sciatic nerve (SN) or spinal cord (SC) transection at the T9 level. Red stars indicate lesion site. (H) Kiaa0319 mRNA expression levels 24 h and 1 week after either sciatic nerve (SNI) or spinal cord transection (SCI); unj = uninjured. Results were compared with the uninjured condition and are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.