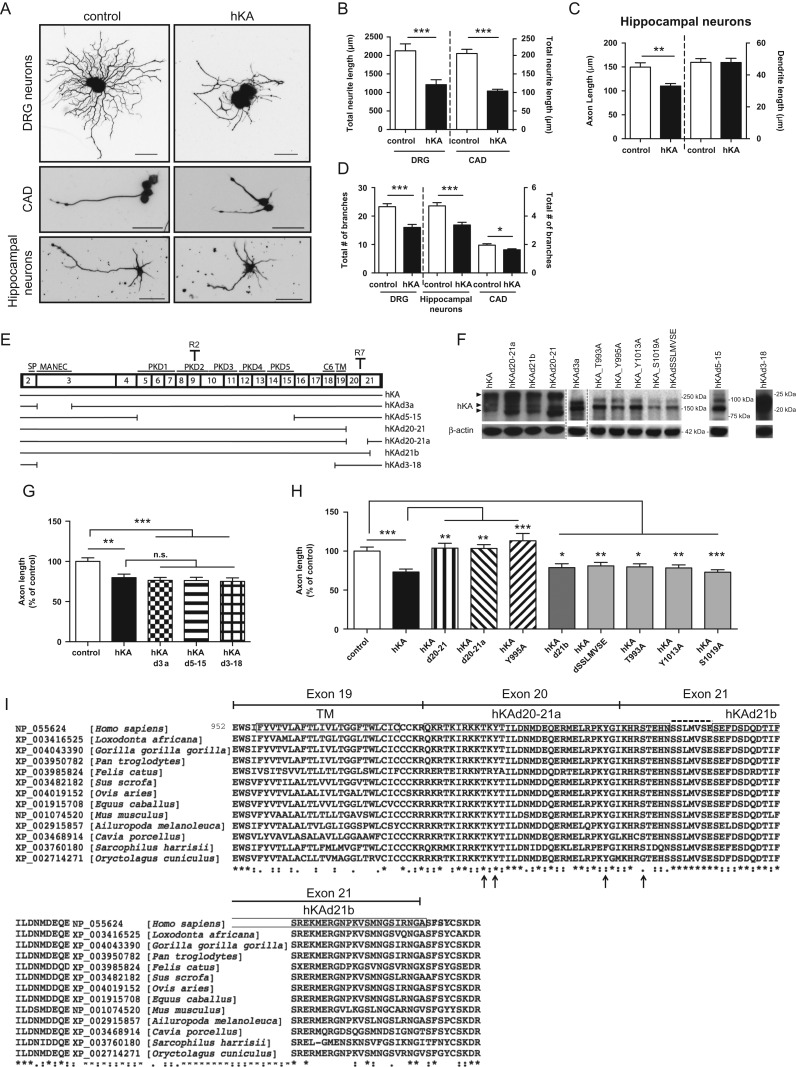
Figure 2.
The initial region of the cytosolic domain of KIAA0319 is necessary for inhibition of axon growth. (A) Representative anti-βIII-tubulin immunofluorescence images of DRG neurons, differentiated CAD cells and hippocampal neurons transfected with either control empty plasmid or full-length human KIAA0319 (hKA); scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Quantification of the total neurite length in transfected DRG (control: n = 75; hKA: n = 50 neurons) and transfected CAD cells (control: n = 162; hKA: n = 152 neurons). (C) Quantification of axon and dendrite length in transfected primary hippocampal neurons (control: n = 105; hKA: n = 71 neurons). (D) Quantification of the total number of segments in transfected DRG neurons (control: n = 68; hKA: n = 40), hippocampal neurons (control: n = 75; hKA: n = 62) and CAD (control: n = 162; hKA: n = 152 neurons). (E) Schematic representation of KIAA0319 constructs (see also Table 1). The numbered upper boxes correspond to the different KIAA0319 exons. In the upper part of the boxes, the region codified is indicated (SP, MANEC domain, PKD domains 1–5, C6 region, and TM domain) together with specific antibody recognition sites for KIAA0319 (R2 in the PKD2 domain and R7 in the cytoplasmic domain). (F) Western blot analysis of KIAA0319 (hKA-upper) with R2 antiserum (R7 antiserum for the 2 far right lanes) and β-actin (lower) in CAD cells overexpressing each of the constructs represented in E. Arrowheads indicate different protein forms commonly detected after overexpression (Velayos-Baeza et al. 2008): dimers (top), fully glycosylated monomer (middle) and partially glycosylated monomer (bottom). Due to the large deletions in the hKAd3-18 and hKAd5-15 mutants a big shift in molecular weight is observed. Molecular weight markers used in each of the gels are shown. (G) Quantification of axon length in hippocampal neurons transfected with control empty plasmid (control; n = 105 neurons), full-length KIAA0319 in pCAGIG backbone (hKA; n = 71 neurons), hKAd3a (n = 66 neurons), hKAd5-15 (n = 60 neurons) and hKAd3-18 (n = 58 neurons). (H) Quantification of axon length in hippocampal neurons transfected with control plasmid (control; n = 64 neurons), hKA (n = 54 neurons), hKAd20-21 (n = 65 neurons), hKAd20-21a (n = 62 neurons), hKA Y995A (n = 57 neurons), hKAd21b (n = 50 neurons), hKAdSSLMVSE (n = 74 neurons), hKA T993A (n = 58 neurons), hKA Y1013A (n = 61 neurons) and hKA S1019A (n = 63 neurons). (I) Sequence alignment of the TM domain and cytosolic tail of mammalian KIAA0319 proteins (encoded by exons 19–21 of the human gene, as shown on top). The accession number of each species is depicted. Strongly conserved positions are shown below the sequence, as annotated by the alignment software: (*) single, fully conserved residue; (:) residues with strongly similar properties; (.) residues with weakly similar properties. Boxes in the human sequence represent the TM domain and the regions deleted in hKAd20-21a and hKAd21b mutants. The SSLMVSE sequence is highlighted above the alignment with a dashed line. Putative phosphoresidues predicted using PhosphoNET are highlighted with arrows, below the alignment. Results are expressed in mean ± SEM * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not statistically significant.