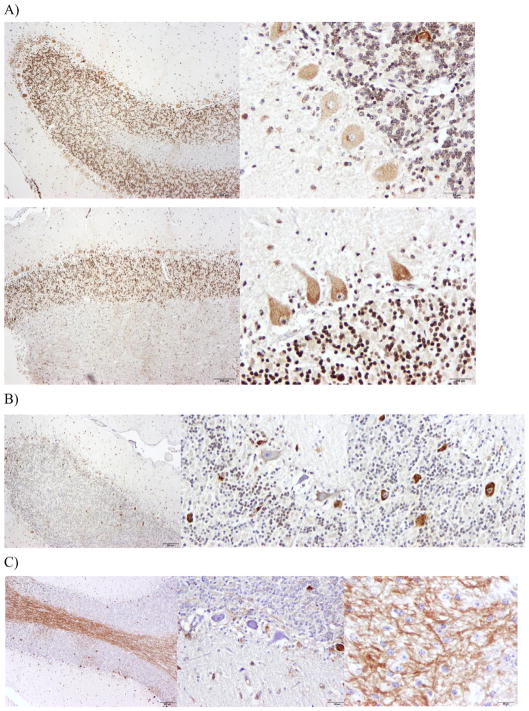
Fig. 3.
Differential localization of MUTYH in control (A) and CA-affected horses (B, C). Using the primary antibody rabbit anti-MUTYH (LS-C354036, LifeSpan Biosciences, Inc) and the secondary biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG, with DAB staining for visualization. Healthy horses show cytoplasmic staining in Purkinje neurons and nuclear staining in granular neurons for MUTYH (A). CA-affected horses show two patterns of localization for MUTYH. One pattern is cytoplasmic staining in Purkinje neurons and nuclear staining for superficial layer of granular neurons for MUTYH (B). The other pattern is random cytoplasmic staining in Purkinje neurons, no staining in the granular neurons and intense staining of the white matter (C).