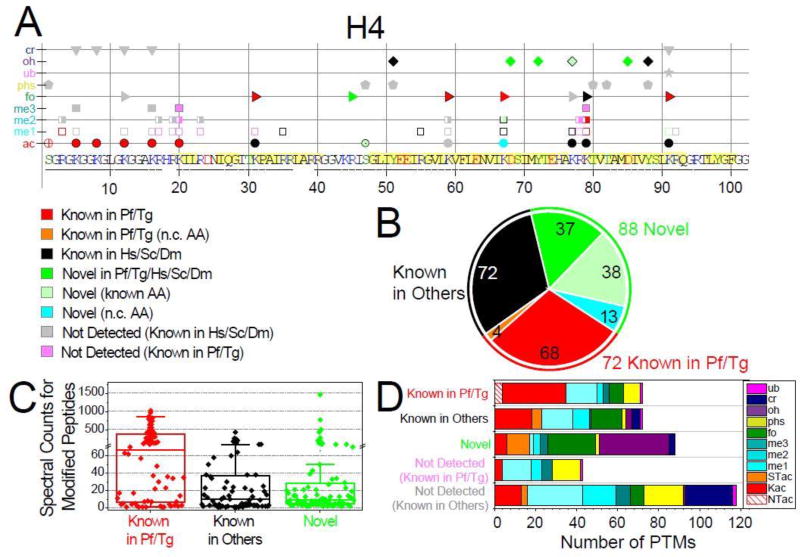
Figure 1. Qualitative overview of Plasmodium histones modifications.
A. Detected PTMs on Plasmodium histone H4 are plotted along its sequence, while the plots for H2A, H2A.Z, H2B, H2B.Z, H3, and H3.3 are provided in Fig. S1. PTMs are sorted into three main categories based on their novelty status (see SI-3.1): 1) PTMs previously reported in Plasmodium falciparum and/or Toxoplasma gondii (red and orange symbols for non-conserved (n.c.) residues); 2) PTMs previously reported in species other than apicomplexans (black symbols); 3) novel PTMs on conserved residues are in bright green symbols, a subset of those are in lighter green symbols drawn with a black edge to denote that the amino acid had been previously reported as modified by other types of PTMs, while novel modifications on n.c. residues are in cyan. In addition, PTMs previously reported in other organisms but were not detected (n.d.) in our analysis are plotted as grey symbols, while PTMs previously detected in apicomplexans are colored in light pink (SI-3.1). Underlined amino acid residues are covered by detected peptides. Amino acids predicted to be within structured domains (SI-3.2) are highlighted in yellow. B. Total numbers of PTMs for each of the novelty categories. C. Spectral counts for peptides bearing the 232 detected PTMs within each of the novelty categories. D. Tally of the PTMs types falling into each of the novelty categories and the known PTMs not detected in our analysis.