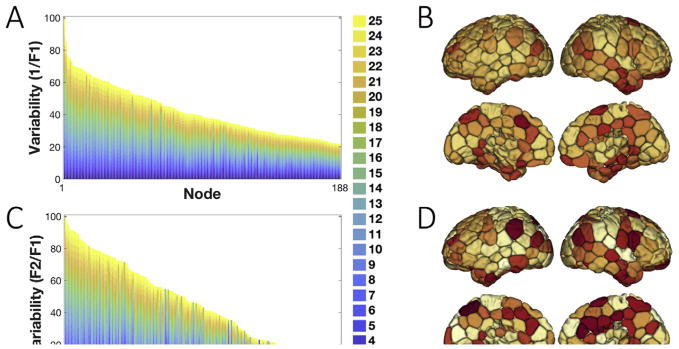
Fig. 5. Inter-individual variability measured by the first and second votes in the majority voting.
A) The inverse F1 is displayed for all the cortical nodes in the brain, sorted from high to low. For all numbers of networks (K = 2, …, 25), inverse F1 measures are collapsed, scaled, and depicted in a barplot. As F1 measures the number of individuals who voted for the group-vote node-to-network assignment, the inverse F1 is a measure of variability between individuals and the group, with a higher measure indicating higher variability and lower confidence. B) The inverse F1 depicted on the brain after summing over all numbers of networks. C) The ratio between the second (F2) and the first (F1) vote for the node-to-network assignments is displayed for all cortical nodes in the brain, sorted from high to low. Similarly, the F2:F1 ratio is a measure of variability across individuals, as a high F1 and a low F2 corresponds to a confident network assignment reproduced across individuals. The barplot displays the corresponding measure for all numbers of networks (K = 2, …, 25) stacked on top of each other and scaled to the range (0,100). D) F2:F1 ratio depicted on the brain after summing over all numbers of networks. The higher-order association areas in the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes display higher inverse F1 and F2:F1 ratio values compared to primary-sensory areas.