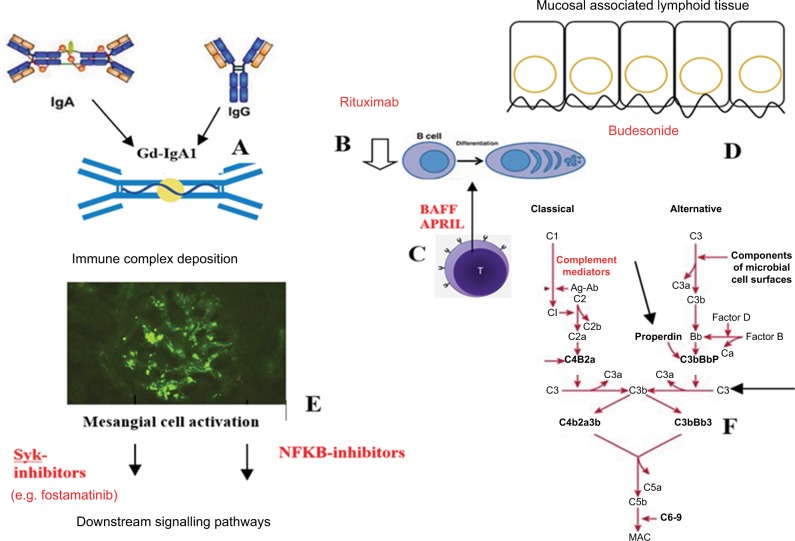
Figure 2.
Pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets in IgA nephropathy.
Notes: (A) Development of IgG and/or IgA autoantibodies against polymeric galactose-deficient IgA1. (B) B-cell depletion of autoantibody-producing plasma cells using rituximab. (C) Targeting BAFF or APRIL. These may be involved in promoting B-cell class switch to IgA1-producing plasma cells. (D) Using budesonide to target dysregulation of the mucosal immune system. (E) Targeting mesangial cell activation and production of inflammatory mediators such as via Syk or NF-kB. (F) Targeting elements of the complement cascade such as properdin or C3.
Abbreviations: APRIL, a proliferation-inducing ligand; BAFF, B-cell activation factor of the TNF family; MAC, membrane attack complex; NF-kB, nuclear factor-kappa B; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase.