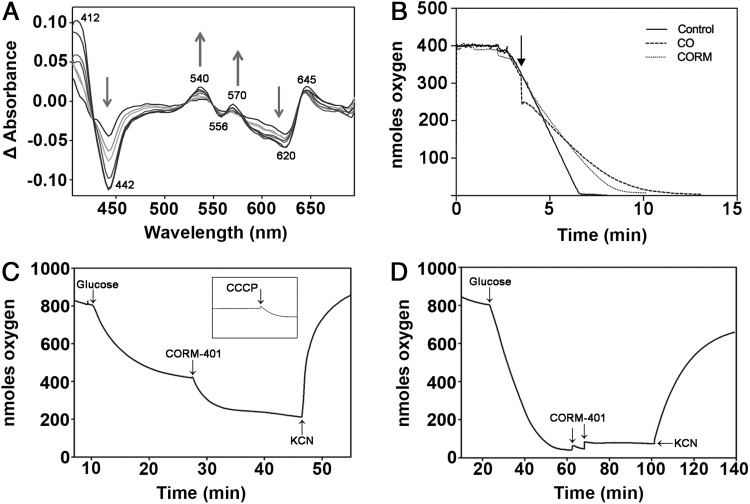
FIG. 7.
CO released from CORM-401 binds terminal oxidases in whole cells, but exhibits uncoupler-like activity on respiration. (A) Cells were grown in LB media to the exponential phase and concentrated in PBS to an OD of ∼55. CORM-401 was added to a final concentration of 100 μM. CO difference spectra were recorded over 15 min; arrows show the direction of absorbance increase or decrease in successive scans. (B) Membrane particles (60 μg protein/mL) from wild-type E. coli were added to a closed electrode chamber. Respiration was stimulated by addition of NADH and when air saturation had reached ∼75% of the initial (arrow), CO saturated solution (dashed line) or CORM-401 (final concentration 100 μM) was added (gray dotted line). Respiration of membranes in the absence of any compounds was followed as a control (solid line). (C) Cells were grown to the mid-exponential phase (OD600nm ∼0.6) in Evans medium and resuspended in Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.4, before analysis in an open oxygen electrode. Where indicated by arrows, glucose was added to stimulate respiration and cells respired until a steady state was reached before addition of 100 μM CORM-401. Inset shows 10 μM CCCP added under equivalent conditions. (D) Partial inhibition of respiration was observed at low oxygen tensions when CORM-401 was added twice (arrows marked CORM-401). In (C) and (D), KCN was added at the arrows at the end of the experiment to the chamber to a final concentration of 1 mM to fully inhibit respiration. All data are representative of three biological repeats.