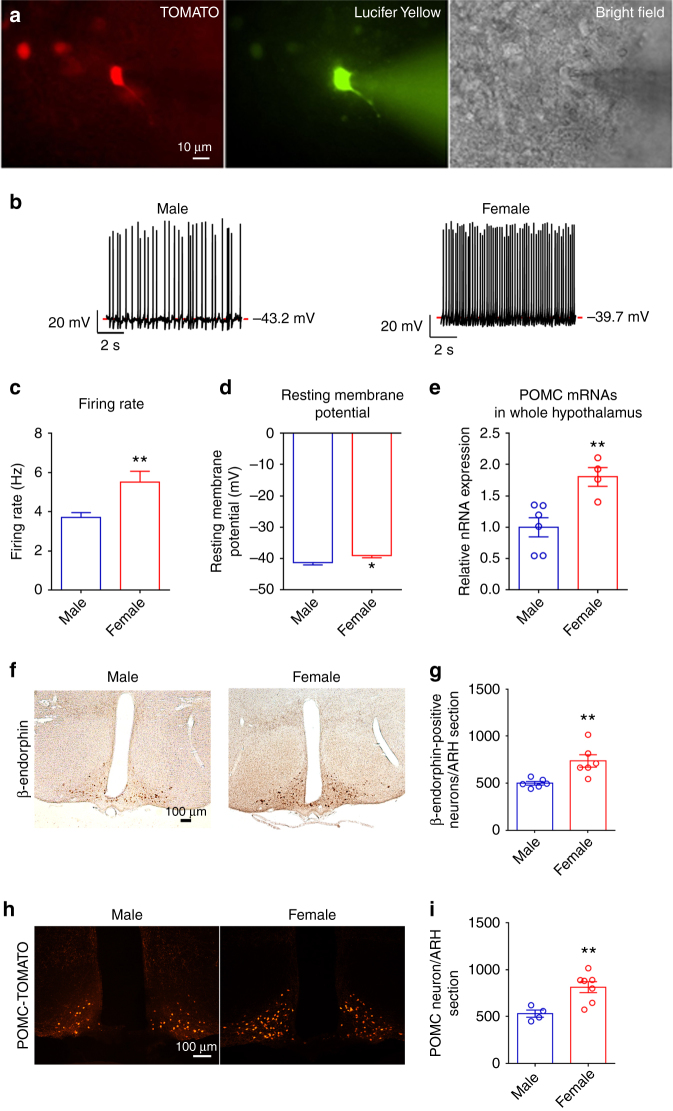
Fig. 1.
POMC neurons display sexual dimorphism in neural activities and gene transcription. a Fluorescence for TOMATO (left) and Lucifer Yellow (middle), and bright-field illumination (right) of the recorded POMC neuron in a brain slice prepared from POMC-CreERT2/Rosa26-tdTOMATO mouse with tamoxifen induction at 11 weeks of age. b Representative current clamp traces in POMC neurons from chow-fed male or female POMC-CreERT2/Rosa26-tdTOMATO mice at the age of 15–16 weeks. c, d Average firing rate (c) and resting membrane potential (d) in POMC neurons from male or female POMC-CreERT2/Rosa26-tdTOMATO mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. N = 37–78 per group. *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01 in t-tests. e POMC mRNAs levels in the entire hypothalamus from male or female littermates (16 weeks of age), quantified by RT–qPCR. Data are presented as mean ± SEM with individual data points. N = 4 or 6 per group. **P < 0.01 in t-tests. f Representative immunostaining images for β-endorphin in the hypothalamus of male or female littermates (16 weeks of age). g Quantifications of β-endorphin-positive neurons in the hypothalamus from 1 out of five consecutive brain sections of male or female littermates. Data are presented as mean ± SEM with individual data points. N = 6 per group. **P < 0.01 in t-tests. h Representative fluorescent images for TOMATO in the hypothalamus of male or female POMC-CreERT2/Rosa26-tdTOMATO littermates (tamoxifen injected at 11 weeks of age, and perfused at 16 weeks of age). i Quantifications of TOMATO-positive neurons (POMC neurons) in the hypothalamus of one out of five consecutive brain sections of male or female littermates (tamoxifen injected at 11 weeks of age, and perfused at 16 weeks of age). Data are presented as mean ± SEM with individual data points. N = 4 or 7 per group. **P < 0.01 in t-tests