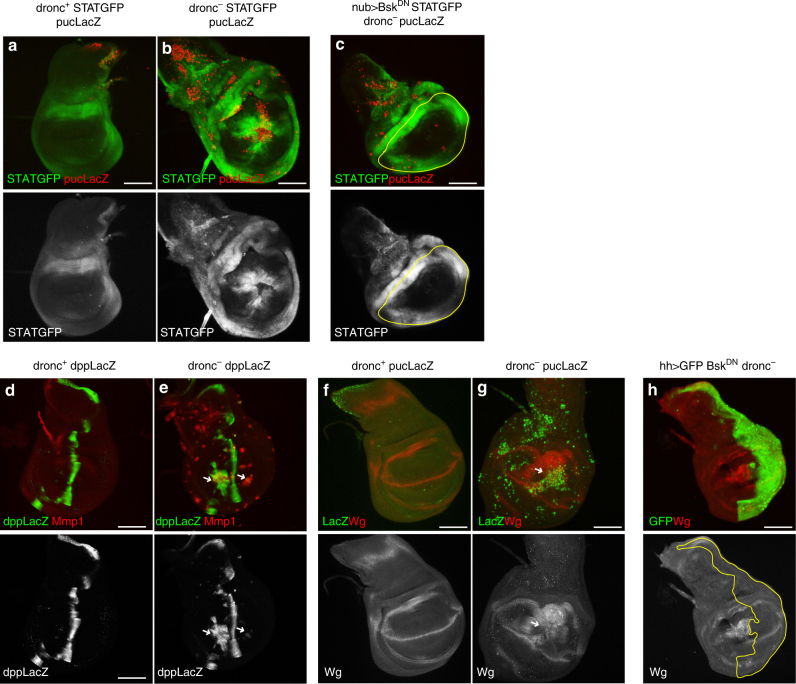
Fig. 3.
JNK persistent activity induces sustained activity of the JAK/STAT, Dpp and Wg pathways. a–c Images of wing discs of genotypes: a STAT-GFP;pucLacZ dronci24/+(n = 15), b STAT-GFP pucLacZ dronci24/dronci29 (n = 29), c UAS-BskDN;nub-Gal4/STAT-GFP;puc-lacZ dronci24/dronci29 (n = 3), 96 h after irradiation stained for STAT-GFP (green) and β-gal (red). Note in b the ectopic STAT expression, especially in the wing pouch, associated with ectopic JNK activity. In c, the suppression of JNK, achieved by forcing bskDN in the wing pouch (the domain of nubbin outlined in yellow), prevents ectopic STAT expression. d, e Images of wing discs of genotypes: d dpp-LacZ;dronci24/+(n = 14) and e dpp-LacZ;dronci24/dronci29 (n = 17) 96 h after irradiation; dpp expression is monitored by a LacZ insert at the dpp locus (dpp-LacZ, green) and JNK function is indicated by Mmp1 staining (red). The dronc+ disc (d) shows wildtype dpp pattern, whereas in dronc− (e) there is ectopic dpp expression (arrows) associated with Mmp1 cells. f, g Images of wing discs of genotypes: f pucLacZ dronci24/+ (n = 9), g puclacZ dronci24/dronci29 (n = 22) 96 h after irradiation, stained with anti-Wg antibody (red) and puc-LacZ (green) to label JNK activity. The wg expression pattern is normal in dronc+ (f), but in dronc−, there is clear ectopic expression (g), especially in the wing pouch (arrow). Note the overall coincidence between the zones of ectopic wg expression and of JNK activity. And h UAS-bskDN;UAS-GFP;puc-lacZ dronci24/hh-Gal4dronci29 (n = 8) 96 h after irradiation, stained with anti-Wg antibody (red), the suppression of JNK activity by bskDN in the posterior compartment (green) prevents ectopic wg expression. Scale bars are 100 μm