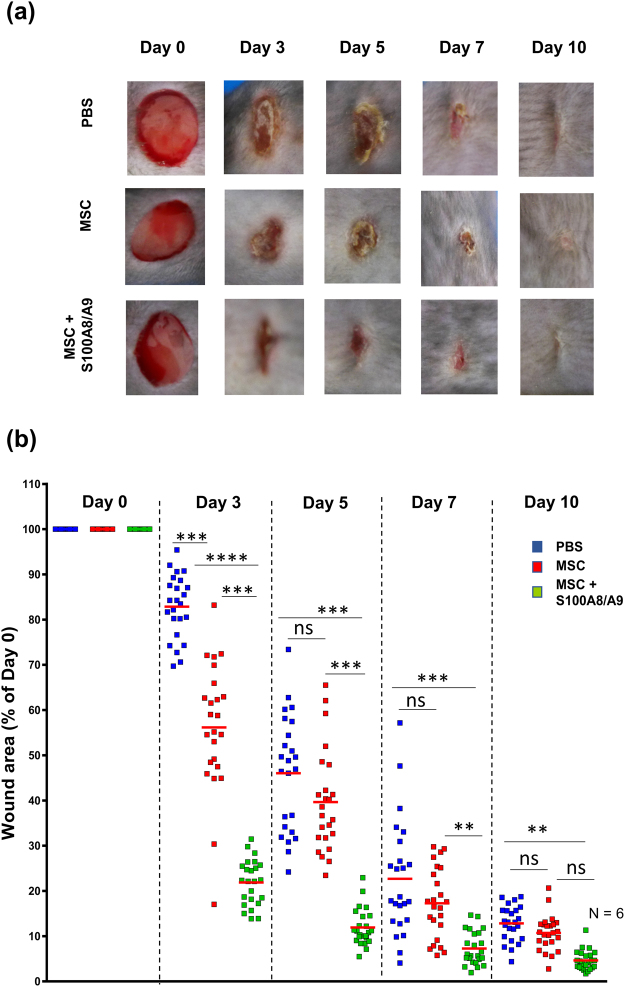
Figure 1.
S100A8/A9 activated MSCs significantly accelerate wound healing. Full-thickness excisional wounds including the panniculus carnosus were produced on the back of mice by 6 mm biopsy round knives. Wounds margins were intradermally injected with PBS or with 2.5 × 105 MSCs (either non-treated or treated with S100A8/A9) or PBS. Each wound was digitally photographed at the indicated time points, and wound areas were analyzed using Adobe Photoshop. (a) Representative macroscopic pictures of PBS or MSC or MSC treated with S100A8/A9 wounds at day 0 and 3, 5, 7 and 10-day post-wounding. (b) Quantitative analysis of 24 wound areas per group, representing wound closure as percentage of the initial wound size at day 0. Blue symbols represent wound sizes of the PBS treated group, red symbols represent wound sizes following intradermal MSC injection and green symbols represent wound sizes following injection with MSCs pre-activated with 0.5 µg/mL Rh S100A8/A9 protein. The red line in each group represents the mean value of 24 wounds from 6 mice. The significance among the groups were calculated using ANOVA with non-parametric measures using Kruskal Wallis and Dunns’ post hoc test where *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 ns, non-significant.