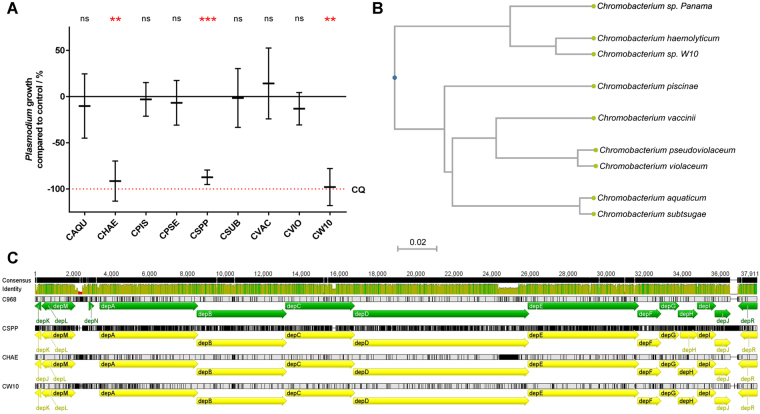
Figure 2.
Anti-Plasmodium activity of chromobacteria is restricted to the romidepsin-producing subcluster comprised of C. sp. Panama and C. haemolyticum. (A) Variation in growth of asexual stage P. falciparum NF54 upon incubation with n-butanol extracts of approximately 5 mL of culture supernatants of different Chromobacterium species (LB, 72 h, 30 °C). 0% inhibition is adjusted for parasite growth in vehicle control (1% DMSO) and 100% inhibition is matched to that of 250 nM chloroquine. Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation; significance was determined using a one-tailed one sample t-test to determine whether each treatment significantly lowered parasite growth compared to control (ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). CQ, chloroquine. CAQU, C. aquaticum; CHAE, C. haemolyticum; CPIS, C. piscinae; CPSE, C. pseudoviolaceum; CSPP, C. sp. Panama; CSUB, C. subtsugae; CVAC, C. vaccinii; CVIO, C. violaceum; CW10, C. haemolyticum W10. (B) UPGMA tree generated from a distance matrix inferred from pairwise genome average nucleotide identity (gANI). A distance of 0.02 indicates that the gANI of two species differs by 2 percent points. Cophenetic Correlation Coefficient (CP) = 0.997961877789881. (C) Alignment between the reference romidepsin biosynthetic gene cluster in C. sp. 968 (C968; GenBank: EF210776.1) to the ones present in the genomes of C. sp. Panama (CSPP) and C. haemolyticum, both MDA0585 (CHAE) and W10 (CW10) strains. Geneious alignment in Geneious v5.4 (global alignment with free end gaps; cost matrix: 65% similarity).