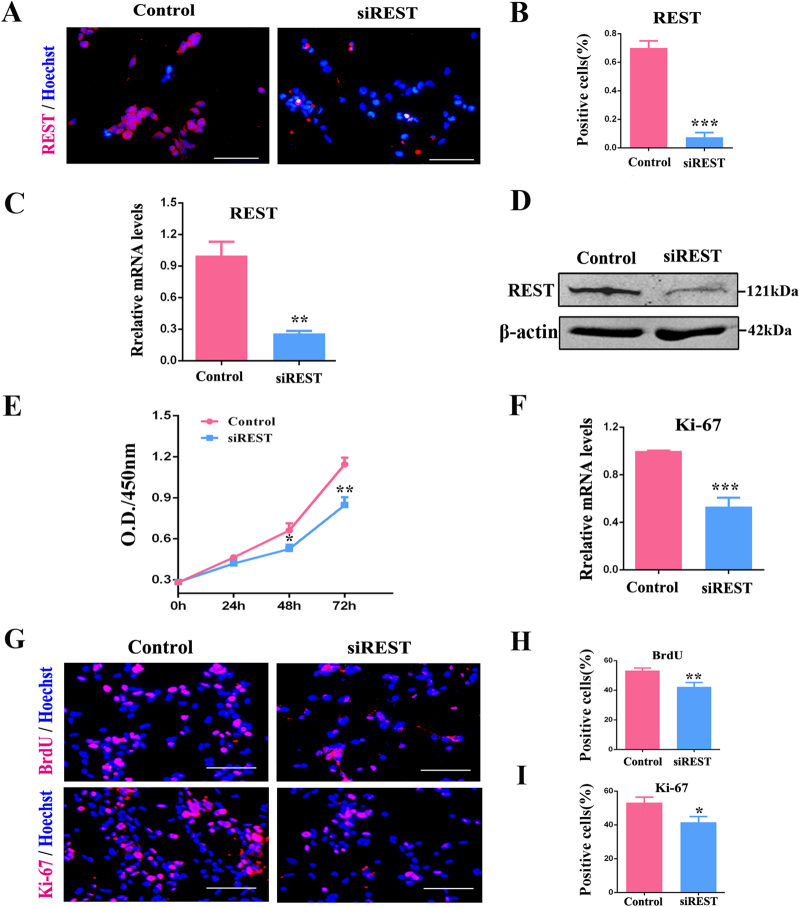
Fig. 1. siREST inhibits RPC proliferation.
a, b The immunocytochemistry, c qPCR analysis and d western blot results revealed that the expression levels of REST decreased in the siREST-treated RPC cultures compared with the control. e The proliferation ability of the RPCs was assessed via CCK-8 analysis. The proliferation ability of the RPCs markedly decreased after treatment with siREST under proliferation conditions. f According to the qPCR analysis, expression levels of Ki-67 decreased significantly in siREST-treated RPC cultures. g-i Immunocytochemistry with antibodies against BrdU and Ki-67 revealed the effects of siREST on RPC proliferation and was consistent with the results shown above. Scale bars: 100 μm. Data are the averages of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. *P ≤ 0.01, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 (Student’s t-test)