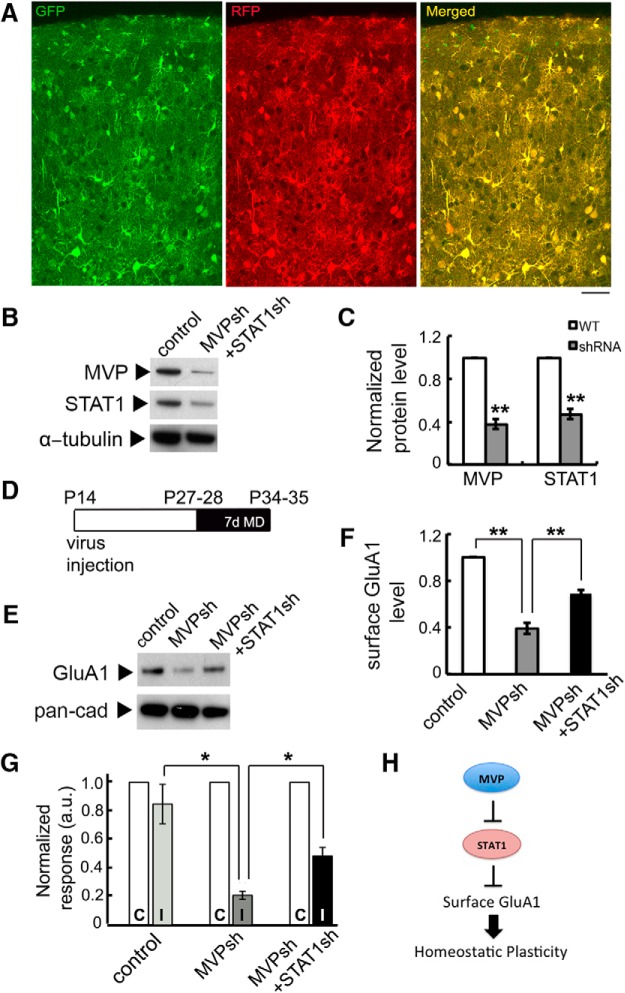
Figure 5.
Normalization of STAT1 level partially rescues deficits in surface GluA1 expression and open-eye responses induced by MVP-knockdown after long-term MD. A, GFP and RFP expressed in virus-infected cells across cortical layers of mouse V1. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, C, Expression of MVP and STAT1 and its quantification in the visual cortex of mice injected with MVPsh and STAT1sh compared with control mice injected with GFP and mCherry-expressing viruses (n = 3 animals each). Lysates were collected from P35 animals. D, Timeline of virus injection and eyelid suture in the surface biotinylation assay and optical imaging experiment. E, F, Expression of cell surface GluA1 after 7d MD and its quantification in V1 of mice injected with scramble control, MVPsh or MVPsh+STAT1sh viruses (n = 3 animals each). Lysates were collected from P35 animals. G, Quantification of the normalized ipsilateral open-eye response after 7 d MD (n = 3 animals each). C, Contralateral eye response; I, ipsilateral eye response. Averaged data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. H, Schematic summarizing data showing that MVP regulates STAT1 level, which in turn regulates surface GluA1 AMPAR subunits, to enable homeostatic plasticity.