Figure 3.
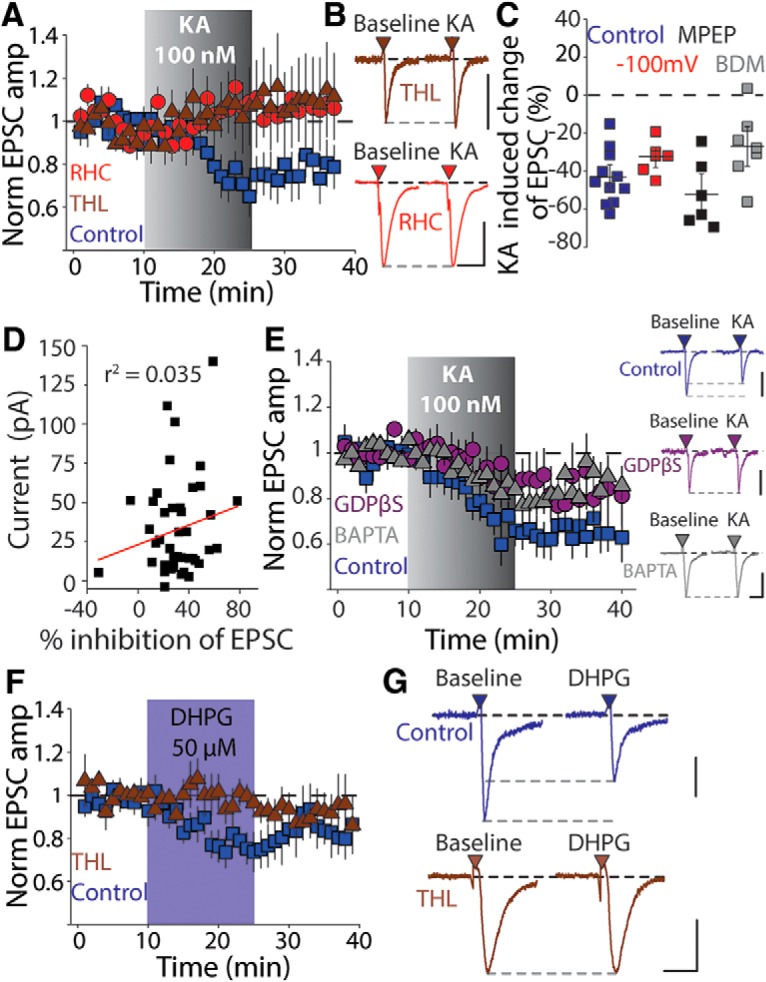
Glutamate receptor activation in dSPNs mobilizes 2-AG. A, Time course of KA-mediated depression in the presence of the DAG-lipase inhibitors RHC (50 μm) or THL (100 μm). B, Representative EPSCs from individual recordings before and after KA application recorded in the presence of THL (top) and RHC (bottom). Calibration: 100 pA, 25 ms. C, Summary plot of KA-mediated depression in experiments in which cells were held at hyperpolarized potentials during KA or the recordings were performed in the presence of the group I mGluR antagonist MPEP (10 μm) or the cell-permeable PKC inhibitor bisindolylmaleimide (BDM, 1 μm). D, Plot of KA-mediated inhibition of corticostriatal EPSCs against the agonist-induced depolarization of dSPNs by 100 nm KA. E, Time course of KA-mediated effects on corticostriatal EPSCs and representative EPSCs in experiments in which the postsynaptic dSPN was dialyzed for 30 min with either GDPβS or BAPTA (17 mm). Calibration: 200 pA, 20 ms (control), 100 pA, 20 ms (GDPβS), 150 pA, 20 ms (BAPTA). F, Time course for experiments in which the group 1 mGluR agonist DHPG (50 μm) was applied in the presence or absence of the DAG-L inhibitor THL (10 μm). Group 1 mGluR activation produced an inhibition of the corticostriatal EPSC amplitude in dSPNs similar to KA. G, Representative EPSCs recorded before and after DHPG application in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of THL. Calibration: 50 pA (top) and 100 pA (bottom), 20 ms.
