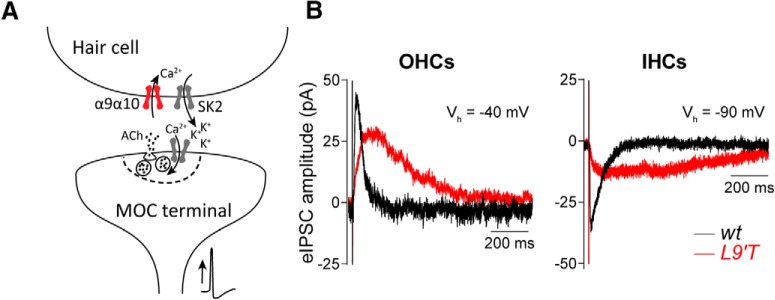
Figure 1.
Characteristics of evoked synaptic currents in OHCs and IHCs from L9′T mice. A, Schematic representation of the cholinergic MOC–hair cell synapse. MOC efferent neurons located in the superior olivary complex of the brainstem project to the cochlea, where they contact the OHCs in hearing mice. Since birth to hearing onset, MOC fibers also transiently innervate the IHCs. Upon nerve stimulation, ACh released from MOC terminals activates the α9α10 nicotinic nAChR. This leads to Ca2+ influx and the subsequent activation of Ca2+-dependent Ca2+-activated SK2 channels. B, Representative traces of eIPSCs in OHCs (left) and IHCs (right) from wt (black) and L9′T (red) mice in response to MOC stimulation at 1 Hz. Vhold was −40 mV for OHCs and −90 mV for IHCs.