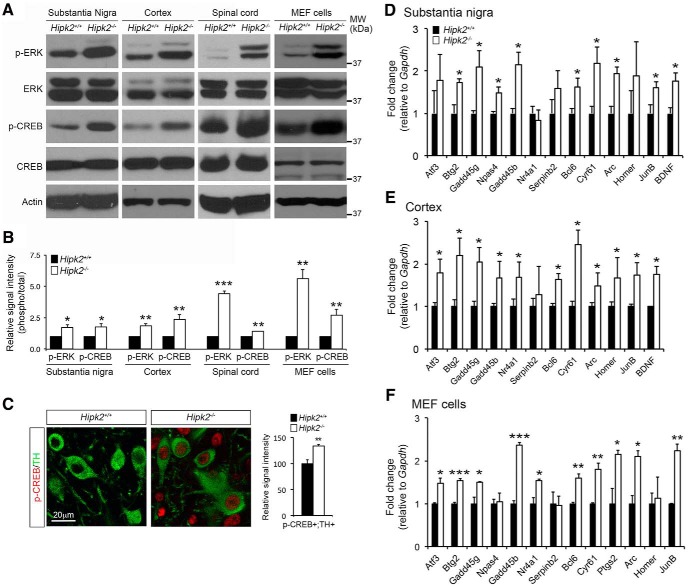
Figure 5.
Enhanced activation of the ERK-CREB signaling pathway in Hipk2−/− mouse brain. A, B, Western blots using protein lysates from the substantia nigra, sensorimotor cortex, and spinal cord of 2-month-old Hipk2+/+ and Hipk2−/− mice showed elevated levels of p-ERK and p-CREB in Hipk2−/− mouse brains, without altering the total level of ERK or CREB. Similar results were identified in cell lysates from Hipk2−/− MEF cells (Figure 5-1. The signal intensity of p-ERK, total ERK, p-CREB, total CREB, and actin was quantified with National Institutes of Health ImageJ software. C, Confocal microscopy showed a significant increase in the relative signal intensity for p-CREB in TH+ DA neuron in the substantia nigra of Hipk2−/− mouse brain. The signal intensity of p-CREB puncta was quantified with National Institutes of Health ImageJ software. D–F, qRT-PCR analyses using mRNA from the substantia nigra and cerebral cortex of 2-month-old Hipk2+/+ and Hipk2−/− mice showed consistent upregulation of several AID genes, and the similar AID genes could also be identified in Hipk2−/− MEF cells. Data are mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 (ANOVA). **p < 0.01 (ANOVA). ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA). Not significant: p > 0.05.