Fig. 3.
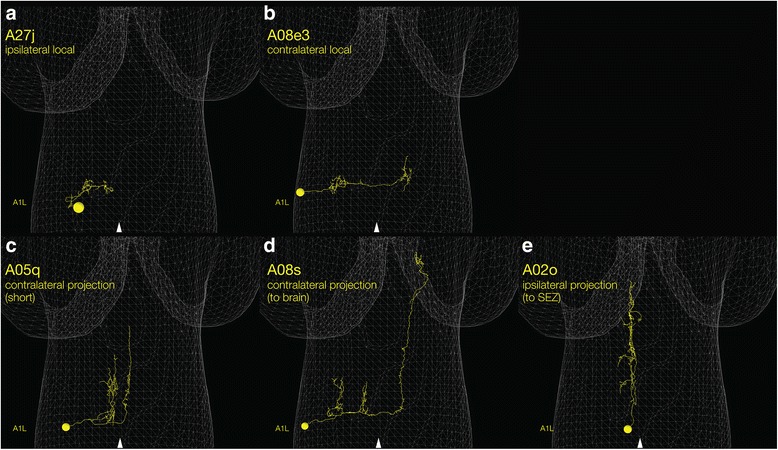
Local and projection interneurons. Examples of local and projection interneurons. There are also descending interneurons with somata in the brain, SEZ, thoracic, or upper abdominal segments (not shown). All panels show a single hemi-segment for clarity (A1 left), although the neurons are bilateral and present in more posterior abdominal segments as well. Midline, arrowhead. (a, b) Local interneurons. A27j is an ipsilateral local interneuron that confines its pre- and post-synaptic arbors to the hemisegment containing its soma [103]. A08e3 is a contralateral local interneuron that projects a process across the midline [16]. Contralateral local interneurons typically have pre-synaptic outputs contralateral to the soma, and post-synaptic inputs on ipsilateral arbors. (c–e) Projection interneurons. A05q is a contralateral projection interneuron that extends anteriorly multiple segments but does not reach the brain [85]. A08s is a contralateral projection interneuron that extends anteriorly to the brain [16]. A02o, also called the “wave” neuron, has a contralateral projection that terminates in the thorax and/or SEZ [82]. Typically, projection interneuron have pre-synaptic outputs at the anterior terminus of the ascending projection, and post-synaptic inputs on the local arbors
