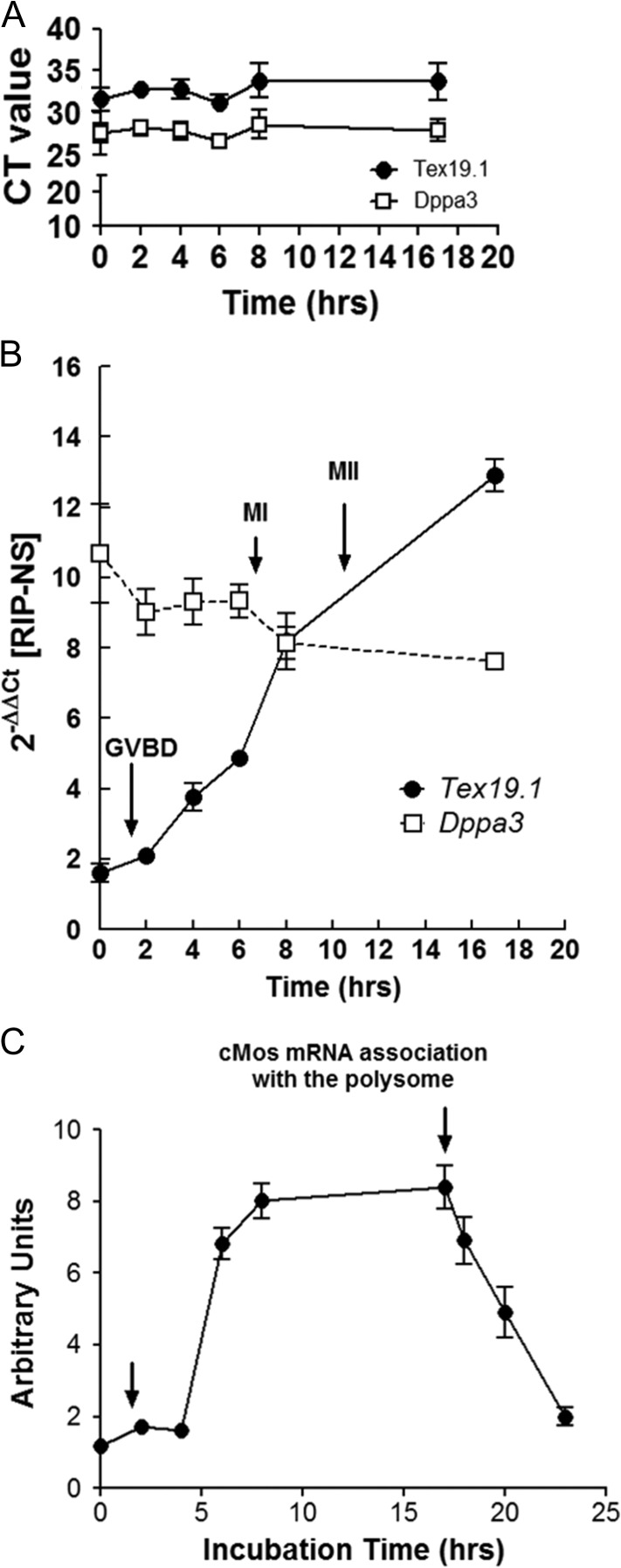
Figure 2.
Contrasting patterns of total mRNA levels versus mRNA bound to ribosomes during oocyte maturation. (A) Levels of the developmental pluripotency associated 3 (Dppa3) and testis expressed 19.1 (Text19.1) mRNA during oocyte maturation. The data were obtained by measuring total mRNA levels by quantitative PCR (qPCR). (B) Dppa3 and Tex19.1 mRNA bound to ribosomes measured by ribosome immunoprecipitation and quantification of the mRNA recovered in the pellet by qPCR. Details of the technique are reported in Sousa Martins et al. (2016). Note that no differences in transcript levels or transcript behavior are detected when using total mRNA (A). However, when mRNAs bound to ribosome are measured, clear differences are found: Dppa3 is constitutively translated during maturation whereas Tex19.1 mRNA translation increases up to 6-fold during oocyte maturation (B). (C) Pattern of ribosome loading on the mRNA coding for Mos, a kinase critical for meiotic maturation. Mos mRNA translation increases after germinal vesicle (GV) breakdown (GVBD), reaches a maximum at the end of metaphase I (MI), remains steady until metaphase II (MII), and its translation is shut off during egg activation. The data are composites of polysome arrays and ribosome immunoprecipitation data.