Fig. 3.
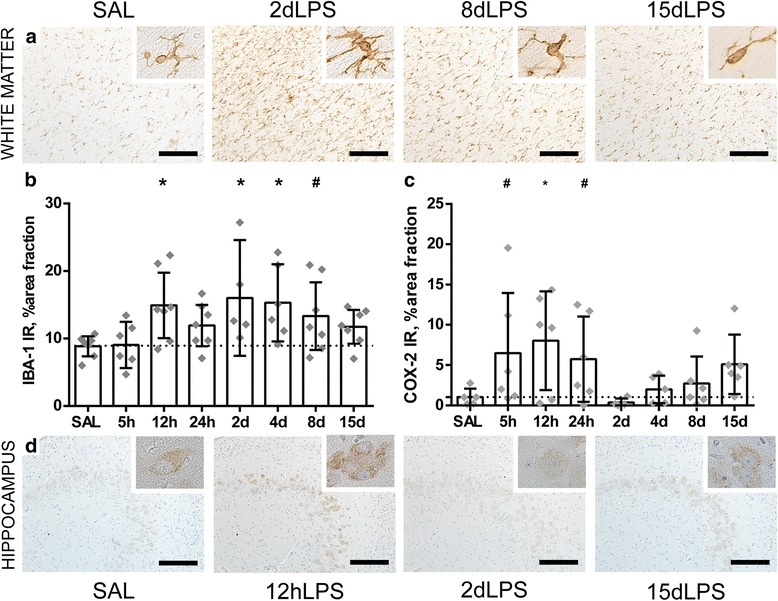
Intra-amniotic exposure to LPS induces an acute, transient cerebral inflammatory response in the preterm white matter and hippocampus. An increase of the area fraction of IBA-1 immunoreactivity (IR) was observed in the white matter at 12 h, 2 days, 4 days, and 8 days following LPS exposure compared to controls (SAL vs. 12 h LPS p = 0.012; SAL vs. 2 days LPS p = 0.006; SAL vs. 4 days LPS p = 0.005; SAL vs. 8 days LPS p = 0.088) (a, b). In the hippocampus, an increase of the area fraction of COX-2 IR was found at 5, 12, and 24 h following LPS exposure (SAL vs. 5 h LPS p = 0.055; SAL vs. 12 h LPS p = 0.016; SAL vs. 24 h LPS p = 0.096) (c, d). Representative histological figures of the IBA-1-positive microglia in animals exposed to intra-amniotic saline (SAL), 2, 8, and 15 days of LPS are shown in a. Representative histological figures of COX-2-positive neurons in the hippocampus of animals exposed to saline (SAL), 12 h, 2 days, and 15 days LPS are depicted in (d). IBA-1 IR and COX-2 IR are depicted as mean % area fraction ± 95% CI. Asterisk indicated p < 0.05 versus control (SAL); number sign indicated 0.05 < p < 0.1 versus control (SAL). Images taken at × 100 magnification (insert at × 400 magnification), scale bar = 200 μm
