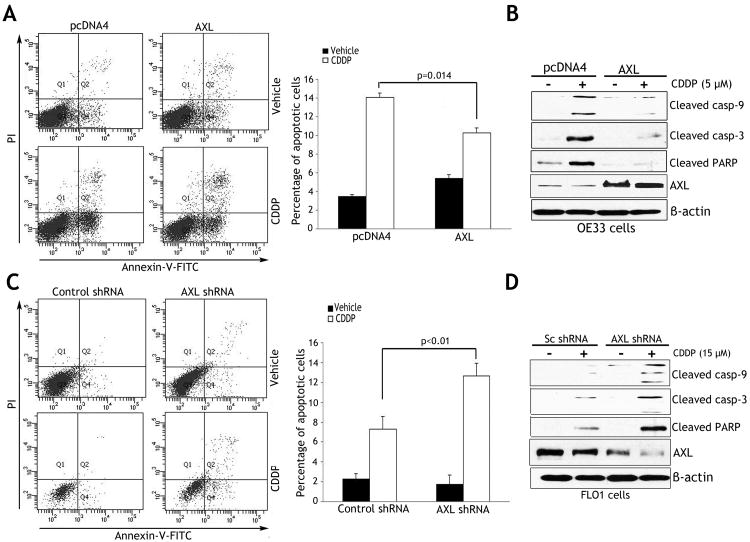
Figure 3. AXL expression inhibits CDDP-induced apoptosis.
A) Apoptosis in OE33 cells stably expressing AXL or empty vector after treatment with vehicle or CDDP (10 μmol/L) for 48h, was determined by Annexin-V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and FACS analysis. Quantitative data (right panel) showed significantly less apoptosis in AXL-expressing cells than control cells (p=0.014) in response to CDDP. B) Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase-3 and -9, cleaved PARP, and AXL proteins in OE33 cells after treatment with vehicle or CDDP as described in panel A. C) Apoptosis in FLO-1 cells stably expressing AXL shRNA or control shRNA after treatment with vehicle or CDDP (15 μmol/L) for 48h was evaluated as in panel A. Quantitative data (right panel) indicated that knocking down endogenous AXL induced significantly more apoptosis than control cells (p<0.01) in response to CDDP. D) Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase-3 and -9, cleaved PARP, and AXL proteins in FLO-1 cells after treatment with vehicle or CDDP as described in panel C. Results are representative of at least three experiments and shown as the mean ± SD.