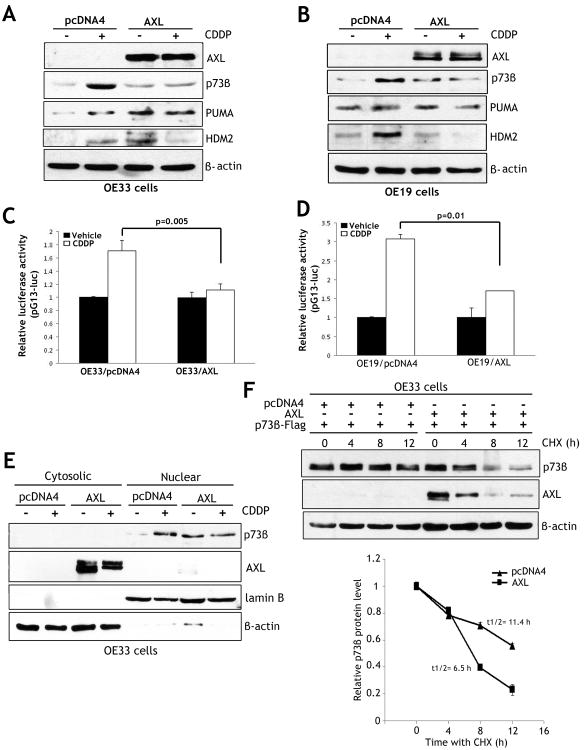
Figure 4. AXL blocks CDDP-induced activation and nuclear accumulation of p73 and decreases its protein stability.
A-B) Western blot analysis of AXL, p73β, PUMA, and HDM2 proteins in OE33 cells stably expressing AXL or pcDNA4, and OE19 cells infected with control adenovirus (10 MOI) or AXL adenovirus (10 MOI). All cells were treated with vehicle or CDDP (10 μmol/L) for 24h. The treatment with CDDP increased levels of p73β, PUMA, and HDM2 proteins, and these effects were abrogated by AXL. C-D) The pG13 luciferase activity was 54.5% higher in OE33/pcDNA4 control cells than OE33/AXL cells (p=0.005), and 81.1% higher in OE19/pcDNA4 control cells than OE19/AXL cells (p=0.01) in response to CDDP. E) Protein accumulation and localization of endogenous p73β in OE33/AXL and OE33/pcDNA4 stable cells was evaluated by Western blot analysis of cytosolic and nuclear protein fractions after treatment with vehicle or CDDP (10 μmol/L) for 48h. AXL expression blocked CDDP-induced nuclear accumulation of p73β. F) Protein stability of exogenous p73β transiently expressed in OE33/AXL or OE33/pcDNA4 stable cells was assessed by Western blot analysis after treatment with 80 μg/ml CHX for the indicated times. The protein degradation results indicate that AXL reduced the protein half-life of p73β from 11.4h to 6.5h relative to control (lower panel).