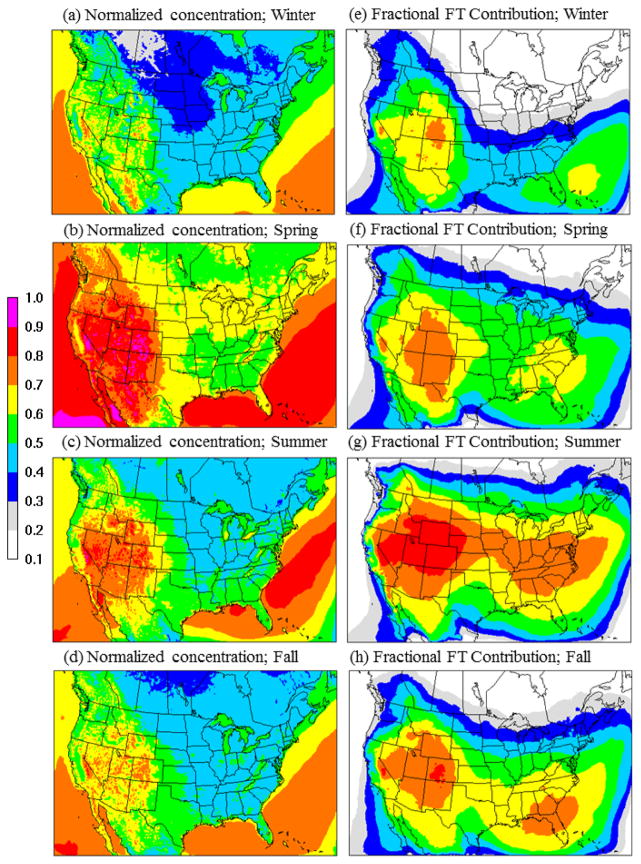
Figure 1.
Impact of lateral boundary conditions (LBC) on simulated seasonal surface-level concentrations. (a–d): Spatial variation in seasonal-mean surface concentrations normalized by the maximum value within the model domain across all seasons. (e–h): Fractional contribution of free-tropospheric (FT) LBCs (specified between 750–250 hPa) to the total LBC-derived concentrations at the surface. Seasons are defined as: Winter (December-February), Spring (March-May), Summer (June-August), Fall (September-November).