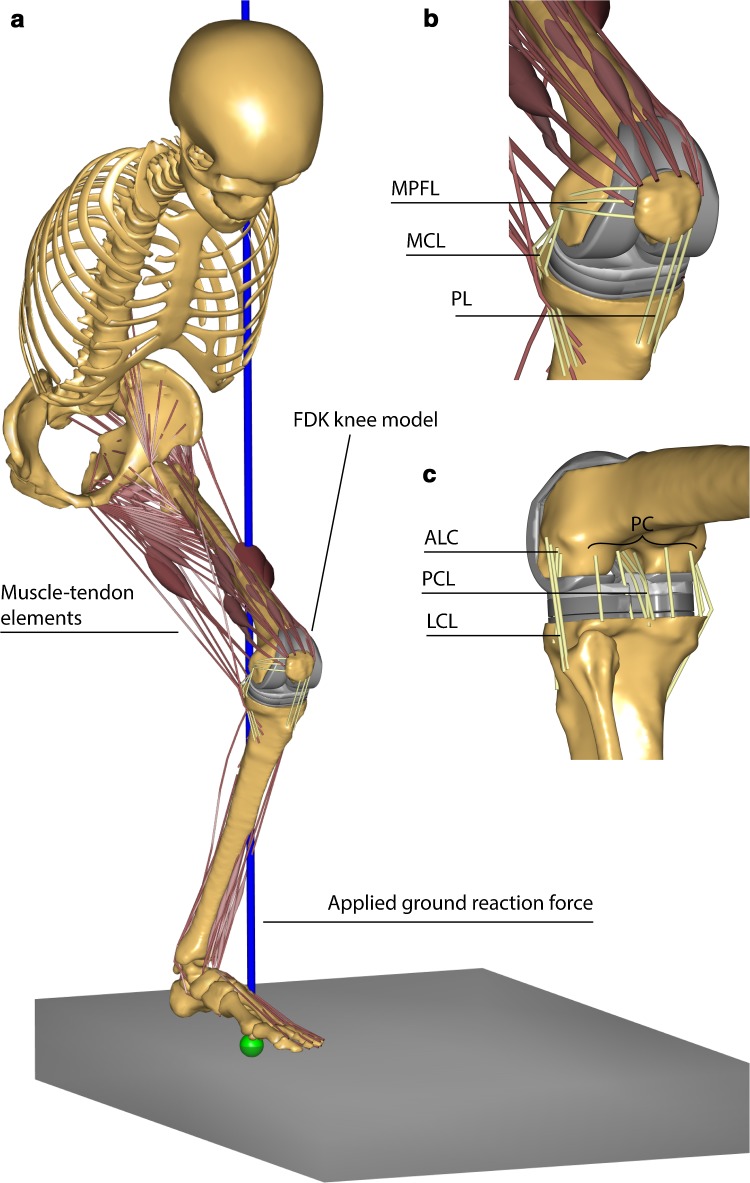
Fig. 1.
A snapshot of the musculoskeletal model used in this study. a The model includes head, trunk and the leg side with the implanted knee. The lower extremity is actuated by 166 muscle–tendon elements. Ground reaction forces and squatting kinematics are applied as input. The tibio- and patello-femoral joints are modelled using force-dependent kinematics (FDK) and include spring ligaments and articular surface contact: b antero-medial view of the knee with medial patello-femoral ligament (MPFL), medial collateral ligament (MCL) and patellar ligament (PL); c postero-lateral view of the knee with antero-lateral complex (ALC), posterior capsule (PC), lateral collateral ligament (LCL)