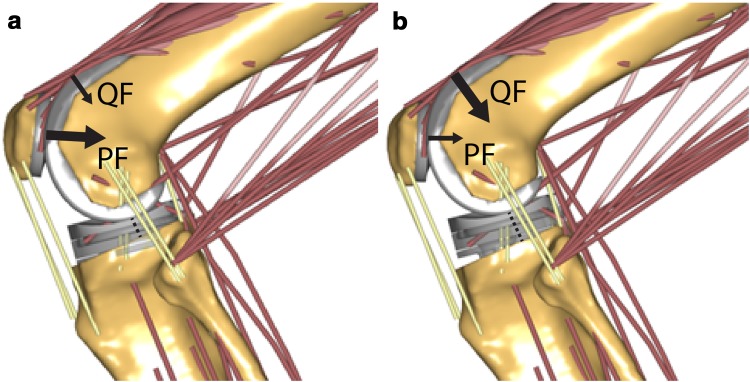
Fig. 7.
Conceptual representation of the quadriceps–femur (QF) and patella–femur (PFJ) load sharing with +9° of tibial slope with a anterior tibial cortex referencing (ACR) and b centre of tibial plateau referencing (CPR) techniques. The quadriceps muscle force decreases with more posterior slope both with ACR and CPR techniques. However, with ACR the position of the patella relative to the femur condyles is higher than with CPR, and a much lower quadriceps force can be transmitted via the quadriceps tendon directly through the femur, thus the patella–femur force is reduced only by a little amount; with CPR technique the amount of quadriceps force transmitted through the femur is higher, thus the patella–femur force is reduced more importantly