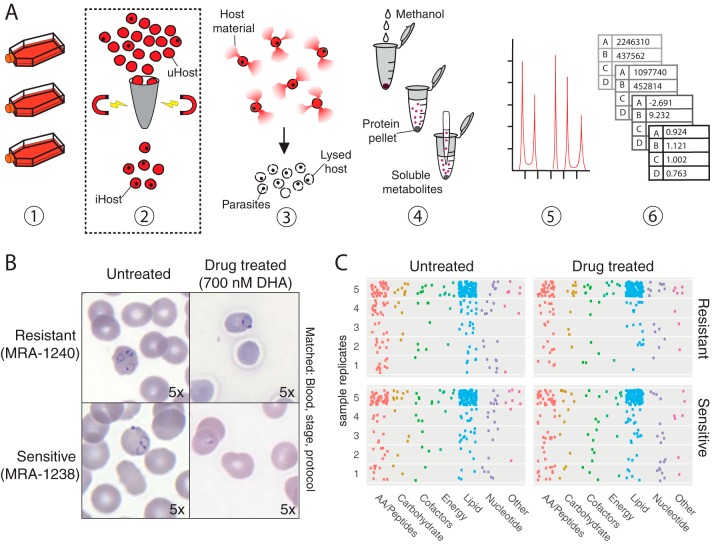
FIG 1 .
Metabolomics pipeline and metabolite identification. (A) Metabolomics purification and analysis pipeline. (Step 1) Laboratory-adapted P. falciparum clones are cultured in host erythrocytes. Parasite count is collected at this step (total erythrocyte number multiplied by percent parasitemia yields total parasite value; see Materials and Methods). (Step 2) If enriching for late-stage parasites is desired, cultures are passed through a magnetic column to retain paramagnetic late-stage-infected erythrocytes. Note that this was not done for the present study. iHost, infected host erythrocytes; uHost, uninfected host erythrocytes. (Step 3) Host erythrocytes are lysed using saponin, but parasites remain intact. Samples are washed to remove hemoglobin and other intracellular host material and quenched on liquid nitrogen. Total protein is quantified at this step (prior to freezing). (Step 4) Soluble metabolites are extracted from precipitated protein using methanol and centrifugation. Double-stranded DNA is quantified at this step. (Step 5) Metabolites are separated via liquid chromatography and identified using mass spectroscopy. Metabolite spectra are compared to a library of authenticated standard metabolites for high-confidence identification. (Step 6) Abundance data for each metabolite are normalized to an appropriate parameter (i.e., DNA content or parasite number), log transformed, centered with respect to the median, and scaled with respect to variances, prior to employing statistical comparisons. (B) Experimental comparison. All samples were grown in RPMI media supplemented with AlbuMAX and hypoxanthine and with one of three blood batches (matched across treatment conditions). At the early ring stage (<3 h postinvasion), 10 samples were treated with dihydroartemisinin (DHA; 700 nM) for 6 h and 10 samples were matched with respect to protocol and condition (blood batch, medium batch, and stage) without drug treatment (see Table S3). Images shown were taken at the 6-h time point (×100 magnification); dormancy was observed at 24 h. (C) Summary of identified metabolites. Metabolites (each represented by one point) from various metabolic subgroups were not uniformly detected in all five replicates for any sample group. How frequently a metabolite was measured across replicates is indicated by the metabolite point placed in data corresponding to 1 to 5 replicates (y axis). The majority of metabolites detected were lipid species, as indicated by the large number of blue dots. A full list of identified metabolites is provided in the supplemental material.