FIG 2 .
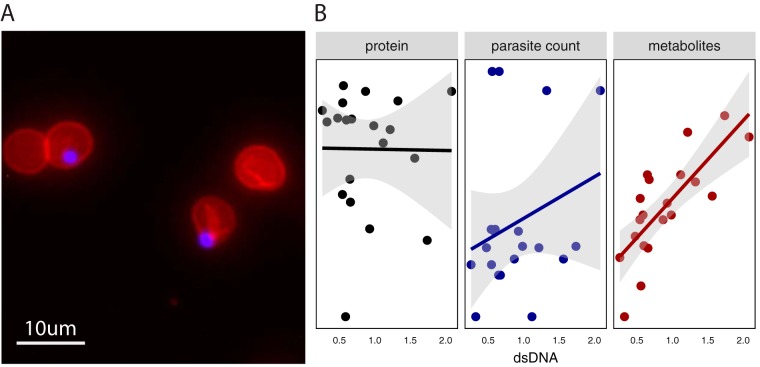
Host persistence is detected using multiple approaches. (A) Visualization of parasites within erythrocyte ghosts. Fluorescent imaging (×40 magnification) reveals parasites (blue, DAPI) retained within erythrocyte ghosts (red, phycoerythrin-conjugated CD235a antibody) following saponin treatment. Approximately 70% of the parasites remain associated with host membranes (see Table S2). (B) Sample characteristics. Samples were evaluated for levels of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA; quantified in micrograms per milliliter on the x axis), protein amounts (black; quantified in micrograms on the y axis [ranging from 67.0641 to 130.0936 μg] in the left panel), and parasite counts (blue; quantified on the y axis [ranging from 1,306,500 to 6,946,875 parasites] in the center panel) prior to analysis. The total number of metabolites detected per sample (red; quantified on the y axis [ranging from 182 to 267 metabolites] in the right panel) was significantly correlated with sample dsDNA quantification (P = 9.8 × 10−5; r2 = 0.76). Protein amount and parasite count were not significantly correlated with dsDNA. The fit line uses a linear model, and the shaded region represents the standard error.