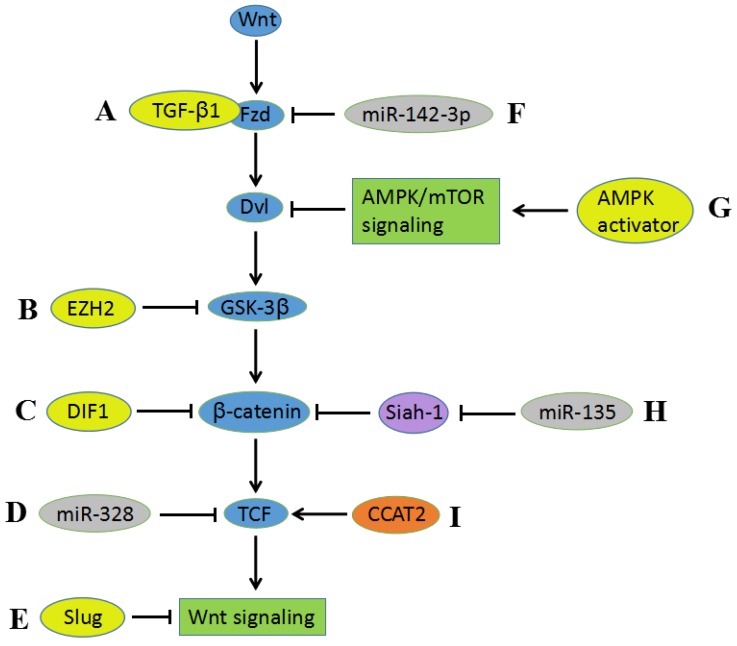
Figure 3.
Cross-talking between Wnt signaling and other biomolecules and signaling pathways. A) TGF-β1 enhances Wnt signaling via Fzd receptors. B) EZH2 activates Wnt/β-catenin by the epigenetic silencing of GSK-3β. C) DIF-1 inhibits Wnt signaling pathway through suppressing β-catenin. D) The suppressive activity of miR-328 in Wnt signaling ascribes to downregulation of TCF. E) Slug can inhibit the activity of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. F) miR-142-3p downregulates Fzd7, resulting in suppressing Wnt signaling activity. G) AMPK activators inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by suppressing DVL protein synthesis via AMPK/mTOR signaling. H) miR-135 downregulates β-catenin via suppressing the expression of Siah-1, thereby contributing to inhibition of Wnt signaling pathway. I) Interaction between CCAT2 and TCF contributes to the activation of Wnt signaling pathway.