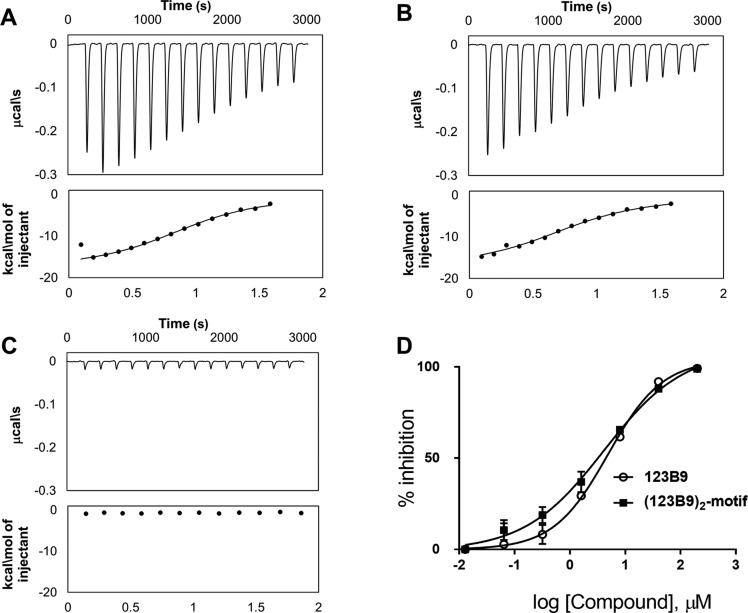
Figure 2.
Biophysical- and biochemical-activity comparisons of 123B9 and the (123B9)2-motif. (A) Isothermal-titration-calorimetry data relative to 123B9 (30 μM) titrated against EphA2-LBD (200 μM), resulting in a dissociation constant of 3.9 μM. (B) Isothermal-titration-calorimetry data relative to the (123B9)2-motif against EphA2-LBD, resulting in a dissociation constant of 4.9 μM. (C) Isothermal-titration-calorimetry data relative to the (123B9)2-motif against EphA4-LBD, showing no significant binding to this closely related ligand-binding domain. (D) Dose–response DELFIA curves for the displacement of biotinylated 123B9 from EphA2-LBD by compounds 123B9 and the (123B9)2-motif (IC50 values of 4.9 and 4.1 μM, respectively).