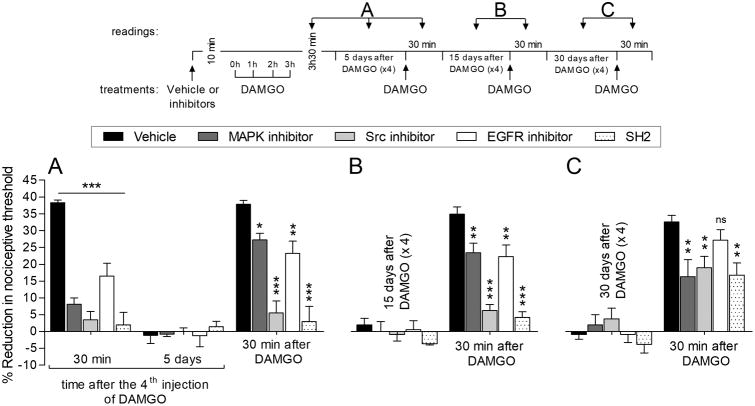
Figure 6. Second messengers in induction of OIH.
Rats were treated intradermally with vehicle (5 μL), MAPK inhibitor (U0126, 1 μg; dark gray bars), Src inhibitor (SU 6656, 1 μg; light gray bars), EGFR inhibitor (tyrphostin AG 1478; 1 μg; white bars) or phosphopeptide SH2 (SH2, which blocks the interaction of Src with FAK and EGFR; 1 μg; dotted bars). The average baseline mechanical nociceptive threshold, before treatments, was 132.3 ± 1.8 g for the vehicle group, 129.9 ± 1.8 g for the MAPK inhibitor, 133.3 ± 1.3 g for the Src inhibitor group, 130.7 ± 1.1 g for the EGFR inhibitor group, and 130.3 ± 2.0 g for the SH2 group. Starting ten minutes later, repeated (hourly × 4) intradermal injections of DAMGO (1 μg) were performed on the dorsum of the hind paw and the mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 30 min after the 4th injection of DAMGO. A. The hyperalgesia induced by the 4th injection of DAMGO was prevented by all inhibitors (F(4,40) = 65.72, *** p < 0.001, when vehicle-treated group is compared to all inhibitor-treated groups; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). Five days later, when the mechanical thresholds were not different from the pre-DAMGO baseline (130.3 ± 1.4 g, t(5) = 2.215; p = 0.0776, for the vehicle-; 130.7 ± 1.2 g, t(5) = 0.5407; p = 0.6119, for MAPK inhibitor; 129.9 ± 1.0 g, t(5) = 1.064; p = 0.3358, for Src inhibitor-; 128.5 ± 2.2 g, t(5) = 1.766; p = 0.1377, for EGFR inhibitor-; and 129.9 ± 1.8 g, t(5) = 0.8596; p = 0.4293, for the SH2-treated group, when the mechanical nociceptive threshold is compared before and 5 days after DAMGO; paired Student's t test), DAMGO (1 μg) was injected at the same site on the dorsum of the hind paw and the mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 30 min later. DAMGO-induced hyperalgesia was partially attenuated in the groups previously treated with inhibitors for MAPK (* p < 0.05) and EGFR (** p < 0.01) and completely inhibited in the Src inhibitor- and SH2-treated groups (F(2,40) = 38.15, *** p < 0.001, when vehicle-treated group is compared to inhibitors-treated groups; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). B. Fifteen days later, when the average baseline mechanical nociceptive threshold was 127.3 ± 2.6 g for the vehicle group, 132.3 ± 1.7 g for the MAPK inhibitor group, 134.3 ± 2.4 g for the Src inhibitor group, 134.3 ± 2.5 g for the EGFR inhibitor group, and 133.3 ± 1.9 g for the SH2 group, DAMGO (1 μg) was injected again on the dorsum of the hind paw. An attenuation on DAMGO-induced hyperalgesia was observed in the groups previously treated with MAPK and EGFR inhibitors (** p < 0.01, when vehicle-treated group is compared to MAPK and EGFR inhibitor-treated groups; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). However, a marked inhibition of DAMGO-induced hyperalgesia was observed in the groups pretreated with the Src inhibitor and SH2 (F(4,20) = 27.13, *** p < 0.001, when vehicle-treated group is compared to Src inhibitor- and SH2-treated groups; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). C. To verify that pretreatment with these inhibitors is able to prevent the induction of OIH, DAMGO (1 μg) was injected again, 30 days after the repeated (hourly × 4) injections of DAMGO. Of note, the average baseline mechanical nociceptive threshold, 30 days after treatments, was 132.0 ± 1.7 g for the vehicle group, 134.0 ± 2.0 g for the MAPK inhibitor, 132.8 ± 1.1 g for the Src inhibitor group, 129.7 ± 2.1 g for the EGFR inhibitor group, and 132.7 ± 1.7 g for the SH2 group. At this time, only a partial attenuation of DAMGO-induced hyperalgesia was observed in the groups previously treated with the MAPK and Src inhibitors, and SH2, when compared to the vehicle-treated group (F(4,40) = 3.47, ** p < 0.01, when vehicle-treated group is compared to MAPK or Src inhibitors- or SH2-treated groups; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). However, no significant (ns) difference was observed between vehicle- and EGFR inhibitor-treated groups (ns, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). These findings indicate a partial contribution of a Src, FAK and MAPK signaling in induction of OIH by repeated exposure to DAMGO. n = 6 paws per group.