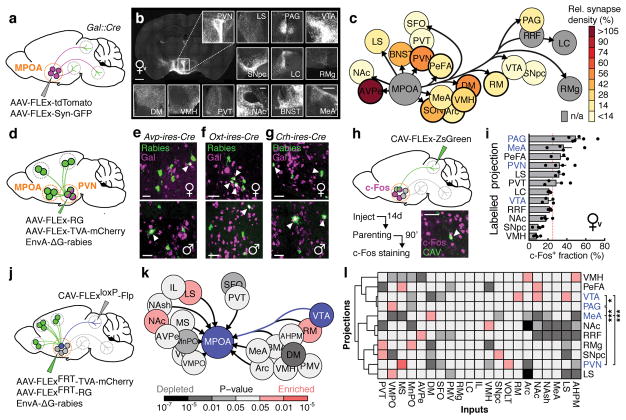
Figure 2. Identification of parenting-activated MPOAGal projections and input-output logic of the MPOAGal circuit.
a, Visualisation of MPOAGal projections. b, MPOAGal projections identified by tdTomato fluorescence. c, Relative synaptic density in MPOAGal projection targets (n = 4, Methods). Grey regions could not be quantified due to tissue autofluorescence. Hypothalamic target areas in bold. d, Monosynaptic retrograde tracing from PVN. e–g, MPOAGal neurons presynaptic to (e) PVNAVP (female 15/364 Gal+, n = 3; male 46/180 Gal+, n = 3) to (f) PVNOXT (female 26/71 Gal+, n = 3; male 7/51 Gal+, n = 3) and to (g) PVNCRH neurons (female 19/72 Gal+, n = 3; male 22/45 Gal+, n = 3). Significantly more MPOA neurons presynaptic to PVNAVP and PVNCRH were Gal+ in males than in females (P < 0.0001, P = 0.0170, two-tailed Fisher’s exact test) whereas more MPOA neurons presynaptic to PVNOXT were Gal+ in females than in males (P = 0.0068). h, Labelling strategy for MPOAGal projections; example of retrogradely labelled c-Fos+ neuron in the MPOA. i, Activated fraction of MPOAGal neurons projecting to parenting-relevant brain areas (n = 7, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 4, from top). Data are mean ± s.e.m. Red line, population average (ref. 3). Projections chosen for further functional studies are highlighted. j, Strategy for monosynaptic retrograde tracing from projection-defined MPOAGal subpopulations. k, l, Map of monosynaptic inputs into VTA-projecting MPOAGal neurons (k) and matrix displaying inputs into projection-defined MPOAGal subpopulations (l, Methods; n = 5, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 3, from top). Tukey post-hoc test assessed whether candidate projections (blue) receive quantitatively different inputs; VTA vs. PAG: *P = 0.0205, PAG vs. PVN: ***P = 0.0002, all other comparisons: ***P < 0.0001. Scale bars, b, left, 500 and inset, 250 μm; e–g, h, 50 μm.