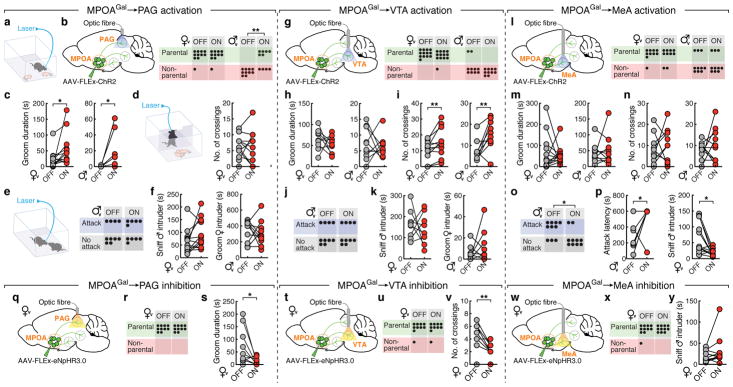
Figure 4. MPOAGal projections mediate discrete aspects of parental behaviour.
a, Setup for optogenetic manipulations. b, g, l, Activation of MPOAGal projections (left); pup-directed behaviour in virgin females and males without (‘OFF’) or with (‘ON’) activation of PAG- (b), VTA- (g) and MeA- (l) projections. c, h, m, Effect of activating PAG- (c), VTA- (h) or MeA- (m) projections on pup grooming (virgin females, n = 13, 9, 10; males, n = 9, 10, 10). d, i, n, Motivation assay (d) and effect of activating PAG- (d), VTA- (i) or MeA- (n) projections on barrier crossing (virgin females, n = 13, 10, 10; males, n = 13, 10). e, j, o, Intruder assay (e) and effect of activating PAG- (e), VTA- (j) or MeA- (o) projections on male-male aggression. f, k, Effect of MPOAGal→PAG (f) or MPOAGal→VTA (k) activation on male- (n = 12, 9) or female-directed (n = 10, 10) behaviour. p, Effect of MPOAGal→MeA activation on male-directed attack latency (n = 10) and chemoinvestigation (n = 10). q, t, w, Inhibition of MPOAGal projections. r, u, x, Pup-directed behaviour in virgin females without (‘OFF’) or with (‘ON’) inhibition of PAG- (r, n = 10), VTA- (u, n = 10) and MeA- (x, n = 11) projections. s, Effect of MPOAGal→PAG inhibition on pup grooming (n = 10). v, Effect of MPOAGal→VTA inhibition on barrier crossing (n = 10). y, Effect of MPOAGal→MeA inhibition male-directed chemoinvestigation (n = 11). Chi-square (b, e, g, j, l, o, r, u, x) or two-tailed paired t-tests (c, d, f, h, i, k, m, n, p, s, v, y), b: **P = 0.0034, c: *P = 0.0273, 0.0374, i: **P = 0.0089, 0.0056, o: *P = 0.0246, p: *P = 0.033, 0.0109, s: *P = 0.0396, v: **P = 0.0038.