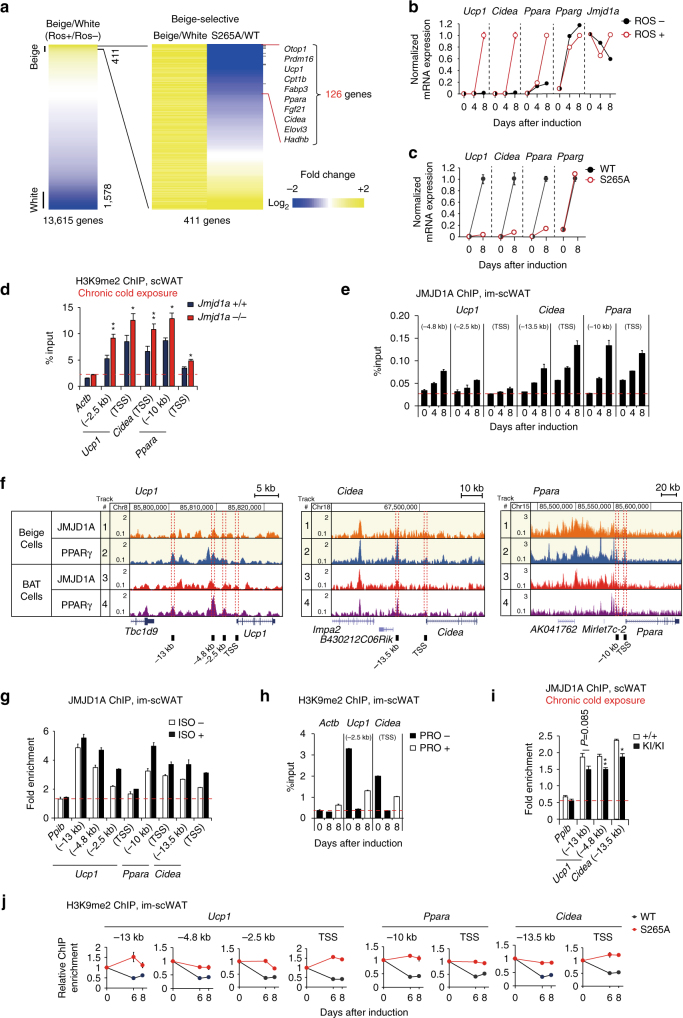
Fig. 5.
JMJD1A demethylates H3K9me2 on beige-selective genes. a RNA-seq heat map depicting expression ratio comparison between beige and white adipocytes, differentiated from im-scWATs under rosiglitazone (ROS) plus or minus condition (left). RNA-seq heat map of 411 beige-selective genes from the left panel depicts comparison of expression ratio between WT-hJMJD1A-transduced and S265A-hJMJD1A-transduced im-scWATs (right). Changes are log2 expression ratios of FPKM, as indicated in a color intensity scale. b, c qPCR analysis of beige-selective genes and Pparg in im-scWATs differentiated with or without ROS (b) or differentiated WT-hJMJD1A-transduced or S265A-hJMJD1A-transduced im-scWATs (c). d H3K9me2 ChIP-qPCR on beige-selective genes using scWAT from age-matched WT (+/+) and Jmjd1a-null (−/−) mice placed at 4 °C for 1 week (n = 4 per genotype group). e JMJD1A ChIP-qPCR on beige-selective genes during ROS-induced beige adipogenesis in im-scWATs. f ChIP-seq profiles for JMJD1A and PPARγ on Ucp1, Cidea, and Ppara genomic regions in differentiated im-scWATs (beige cells) and im-BATs (BAT cells). g, h ChIP-qPCR showing isoproterenol (ISO) treatment increased JMJD1A recruitment in differentiated im-scWATs (g) and the decrease of H3K9me2 levels in beige-selective genes in differentiated beige adipocytes by ROS was blunted by Pro treatment (h). i JMJD1A ChIP-qPCR on beige-selective genes in scWAT of WT and Jmjd1a-S265AKI/KI mice following 1-week cold exposure (WT: n = 3; Jmjd1a-S265AKI/KI: n = 6). j ChIP-qPCR showing the decrease of H3K9me2 levels on indicated beige-selective genes during beige adipogenesis is impaired in S265A-hJMJD1A-transduced im-scWATs. The signal in day 0 of differentiation is set as 1. Data are mean ± s.e.m. of three technical replicates in a representative experiments performed at least three times (b, c, e, g, h, j). Student’s t test was performed for comparisons in d, i. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 were considered statistically significant